Iceland tourism tax climate change is a complex issue. Iceland’s stunning landscapes and vibrant culture draw millions of tourists each year, but this influx presents both economic benefits and environmental challenges. The tourism industry’s reliance on natural resources like glaciers and pristine ecosystems makes it highly susceptible to climate change impacts. This article examines how tourism taxes can play a crucial role in mitigating these effects and fostering sustainable practices.
Iceland’s tourism sector is significant to its economy, offering employment opportunities and boosting revenue. However, the rising temperatures, glacial melt, and increased frequency of extreme weather events pose a threat to the country’s natural attractions. This article will explore the current tourism tax system, its potential for climate change mitigation, and examine the shift towards sustainable practices. We’ll look at how taxes can be utilized to fund renewable energy initiatives and protect Iceland’s precious natural heritage.
Introduction to Iceland Tourism
Iceland, a land of fire and ice, boasts a thriving tourism industry that plays a pivotal role in its economy. From breathtaking landscapes to unique cultural experiences, Iceland draws visitors from around the globe, eager to explore its natural wonders. This industry’s success relies on a careful balance between preserving the environment and maximizing economic benefits.Iceland’s tourism sector is a significant contributor to the national economy, generating substantial revenue and creating employment opportunities.
The industry’s impact extends beyond immediate financial gains, influencing infrastructure development and community well-being. The current state of tourism reflects a complex interplay of factors, including increasing visitor numbers, evolving visitor preferences, and the challenges of sustainability.
Key Features of Iceland’s Tourism Industry
Iceland’s tourism industry is characterized by a focus on natural attractions. The country’s stunning glaciers, volcanoes, geysers, waterfalls, and coastline offer a unique and unforgettable experience. The diverse landscapes, ranging from rugged mountains to serene fjords, cater to a wide range of interests, including adventure seekers, nature lovers, and cultural enthusiasts.
Economic Importance of Tourism
Tourism is a cornerstone of Iceland’s economy. It generates significant revenue through accommodation, transportation, food and beverage services, and guided tours. This revenue supports various sectors, including local businesses and the government. The sector’s impact on employment is also noteworthy, providing jobs for Icelanders across different industries. The contribution of tourism to Iceland’s GDP is substantial, making it a vital part of the national economy.
Current State of Iceland Tourism
The current state of tourism in Iceland is marked by steady growth. Increasing numbers of visitors annually highlight the country’s appeal. However, this growth presents challenges regarding sustainable practices and the potential strain on infrastructure and the environment. The industry faces the crucial need to manage visitor numbers and ensure that tourism remains environmentally and socially responsible.
Types of Tourists Visiting Iceland
Different types of tourists are drawn to Iceland’s unique offerings. Adventure tourists are attracted to activities like hiking, glacier walks, and ATV tours. Nature enthusiasts appreciate the diverse landscapes, from dramatic volcanoes to serene waterfalls. Cultural tourists are interested in experiencing Iceland’s history, traditions, and unique culture. These various interests demonstrate the appeal of Iceland’s diverse attractions.
- Adventure Tourists: These travelers seek adrenaline-pumping experiences, such as hiking challenging trails, exploring glaciers, and participating in extreme sports. The rugged terrain and awe-inspiring landscapes cater to this type of traveler.
- Nature Tourists: Iceland’s breathtaking natural beauty attracts nature enthusiasts. They are drawn to the country’s unique landscapes, including glaciers, waterfalls, geysers, and volcanic hot springs. The tranquility and unparalleled natural wonders cater to this specific type of tourist.
- Cultural Tourists: Iceland’s rich history and cultural heritage captivate visitors interested in learning about the country’s traditions, folklore, and artistic expressions. They may visit museums, historical sites, and cultural events to gain a deeper understanding of the country.
Iceland’s Tourism Tax System
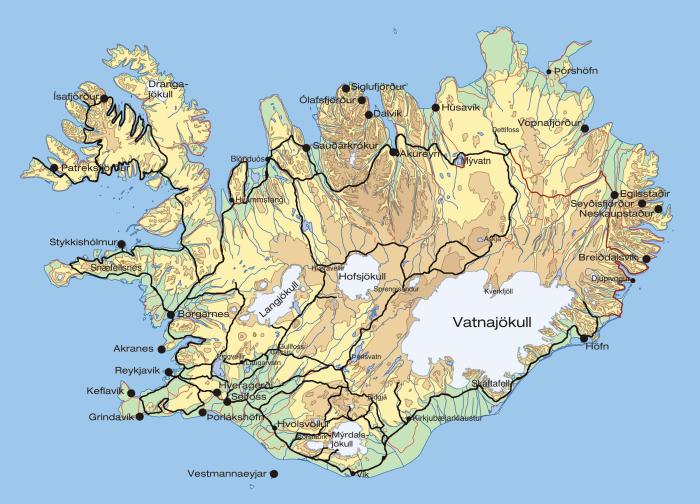
Iceland, a land of breathtaking landscapes and unique experiences, heavily relies on tourism for its economy. This reliance has led to the implementation of a tourism tax system designed to manage the influx of visitors while also contributing to the country’s sustainability efforts. Understanding how this system works is crucial for both tourists and those who wish to support Iceland’s responsible tourism model.Iceland’s existing tourism tax policies are multifaceted, encompassing various levies and charges.
The goal is to ensure the long-term sustainability of the nation’s tourism sector by supporting infrastructure improvements, environmental protection, and the broader well-being of Icelanders. This involves careful consideration of the economic impact on both visitors and the local population.
Tourism Tax Collection Methods
The collection of tourism taxes in Iceland is typically integrated into accommodation costs. This means that visitors often pay the tax as part of their hotel or guesthouse bills. This approach streamlines the process for both tourists and the tax authorities. Furthermore, this embedded approach is often considered more effective for ensuring tax compliance compared to separate, standalone systems.
Tourism Tax Allocation
Funds collected from tourism taxes are meticulously allocated to support specific projects and initiatives. A significant portion is directed towards enhancing the country’s infrastructure, including improving transportation, maintaining roads, and upgrading public amenities. Another portion is often allocated to environmental conservation programs, aimed at preserving Iceland’s natural beauty for future generations. The remaining portion may be used to fund cultural programs and initiatives that enhance the overall visitor experience.
Comparison with Other Tourist Destinations
Iceland’s tourism tax system can be compared to those in other popular tourist destinations, such as Norway and Switzerland. While the specific structures and allocations vary, the underlying principle of utilizing tourism revenue for sustainable development is often shared. The crucial difference lies in the specific priorities and the levels of tax applied. For instance, Norway might prioritize funding specific conservation efforts within national parks, while Switzerland might focus on supporting cultural heritage preservation.
Potential Impacts on Visitor Behavior and Tourism Revenue
Tourism taxes can potentially influence visitor behavior, particularly in terms of accommodation choices and spending habits. Visitors might adjust their travel plans if the tax is perceived as excessively high or if they feel it is not fairly allocated. Therefore, the careful design of a tourism tax system is vital to maintain a positive impact on both the visitor experience and overall tourism revenue.
Studies suggest that a well-structured tax, transparent in its allocation, can potentially encourage responsible tourism and sustainable practices.
Table: Comparison of Tourism Taxes
| Country | Type of Tax | Typical Rate | Allocation Priorities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iceland | Accommodation Tax | Variable, often included in room rates | Infrastructure, environment, cultural initiatives |
| Norway | Accommodation Tax | Variable, often included in room rates | National parks, conservation, cultural heritage |
| Switzerland | Accommodation Tax | Variable, often included in room rates | Cultural heritage, infrastructure, promotion of sustainable tourism |
Climate Change Impacts on Icelandic Tourism: Iceland Tourism Tax Climate Change
Iceland, a land of breathtaking glaciers, geysers, and vibrant wildlife, is increasingly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. The tourism industry, a cornerstone of Iceland’s economy, is feeling the pressure as rising temperatures, glacier melt, and extreme weather events reshape the landscape and alter visitor experiences. This article explores the specific impacts of climate change on Icelandic tourism.The dramatic beauty of Iceland, a major draw for tourists, is intricately linked to its unique environment.
As climate change alters this environment, it directly affects the very experiences that tourists seek. The consequences are multifaceted, ranging from the loss of iconic attractions to changes in the availability of outdoor activities.
Impacts of Rising Temperatures
Rising temperatures in Iceland are causing significant changes to the country’s natural landscapes. Glacier melt is one of the most visible and impactful consequences. This melt affects the accessibility and safety of glacier-based activities like hiking and ice climbing. The receding ice also alters the landscape, potentially exposing previously hidden geological formations or creating new ones.
Glacier Melt Impacts on Tourism Attractions
Glacier melt is dramatically altering the landscape of Iceland, affecting a variety of tourism attractions. Glacier hiking tours, once popular, are becoming less safe and potentially more dangerous. The shrinking size of glaciers impacts the visual appeal, making a once-impressive spectacle a less awe-inspiring one. The meltwater from glaciers can also impact downstream ecosystems, altering river flows and affecting the visibility and experience of waterfalls.
Impacts of Extreme Weather Events, Iceland tourism tax climate change
Extreme weather events, including more frequent and intense storms, are becoming increasingly common in Iceland. These events can disrupt transportation, impacting access to destinations and affecting the safety of visitors. Storms and heavy rainfall can damage infrastructure, including roads and walkways, potentially causing closures and delays. Flooding can affect scenic areas, creating challenges for both tourists and local communities.
Effects of Changing Ecosystems on Tourism Experiences
Climate change is affecting Iceland’s diverse ecosystems. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are impacting plant and animal life, altering the timing of blooming seasons for wildflowers and affecting the migration patterns of birds and marine life. This, in turn, affects the wildlife viewing experiences that are a major draw for tourists. For example, the timing of bird migration might not align with peak tourist seasons, reducing opportunities for observation.
Potential Long-Term Impacts on Icelandic Tourism
The long-term impacts of climate change on Icelandic tourism are potentially severe. The loss of iconic attractions like glaciers and the disruption of ecosystems could significantly reduce the appeal of Iceland as a tourist destination. This could lead to a decline in visitor numbers and a negative impact on the local economy, which relies heavily on tourism. The loss of key attractions will likely lead to a shift in tourist interests, and the need to adapt and diversify tourism offerings.
Iceland’s tourism tax is a hot topic, especially when considering its impact on climate change. While it’s meant to offset the environmental footprint of visitors, it’s complex. Perhaps a luxurious escape to St. Barts, with its stunning hotels, private pools, villas, and pristine beaches, might offer a different perspective on the issue. St.
Barts hotels private pools villas beaches could potentially highlight the trade-offs between tourism’s economic benefits and its environmental costs. Ultimately, finding a sustainable balance for Iceland’s tourism sector remains a key challenge.
Predicted Changes in Tourism Attractions (Next 10 Years)
| Tourism Attraction | Predicted Change (Next 10 Years) |
|---|---|
| Glacier Hiking Tours | Reduced availability due to glacier melt, potential safety concerns. |
| Wildlife Viewing | Changes in migration patterns, altered availability of species. |
| Waterfall Views | Potential changes in water flow, altered visibility due to glacial meltwater. |
| Outdoor Activities | Increased risk of extreme weather events, altered accessibility. |
| Coastal Tourism | Sea level rise, erosion, and potential damage to coastal areas. |
Tourism Tax and Climate Change Mitigation
Iceland’s burgeoning tourism sector, while a vital economic engine, presents unique environmental challenges. Tourism taxes, strategically implemented, can play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change impacts and fostering a more sustainable tourism model. By channeling these funds towards renewable energy, eco-friendly infrastructure, and responsible practices, Iceland can lessen its carbon footprint while ensuring the long-term viability of its tourism industry.Iceland’s tourism tax system offers a powerful tool to support climate change mitigation.
By implementing a dedicated portion of tourism tax revenue towards sustainable practices, Iceland can achieve significant environmental benefits and solidify its position as a global leader in sustainable tourism.
Role of Tourism Taxes in Climate Change Mitigation
Tourism taxes, levied on visitors, can be earmarked for projects that reduce the environmental impact of tourism. This approach ensures that the economic benefits of tourism are balanced with environmental responsibilities. By funding these projects, the tax revenue directly addresses the emissions associated with transportation, accommodation, and activities.
Funding Sustainable Tourism Practices
Tourism taxes can directly fund initiatives that promote sustainable tourism practices. This includes investments in public transportation systems, incentivizing eco-friendly accommodations, and supporting the development of sustainable tours and activities. These measures reduce the environmental impact of tourism while enhancing the visitor experience.
Investing in Renewable Energy and Infrastructure
Tourism taxes can be allocated to upgrading infrastructure and developing renewable energy sources for tourist destinations. This can include installing solar panels on hotels and guesthouses, investing in electric vehicle charging stations, and promoting the use of geothermal energy for heating and transportation. This approach directly addresses the environmental footprint of the tourism industry.
Examples of Successful Tourism Tax Policies
Several countries have successfully implemented tourism taxes to fund environmental protection initiatives. For instance, the UK’s national parks levy encourages responsible behavior in nature-based tourism. Similarly, some European destinations have established dedicated funds for environmental projects, including the preservation of natural habitats and the promotion of sustainable transportation. These examples demonstrate the potential of tourism taxes to drive environmental improvements.
Funding Climate Change Projects in Iceland
| Project | Estimated Cost (USD) | Funding Source (Tourism Tax) |
|---|---|---|
| Upgrade Public Transportation System | 10,000,000 | 50% |
| Develop Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure | 5,000,000 | 25% |
| Promote Eco-Friendly Accommodations | 2,000,000 | 10% |
| Invest in Renewable Energy for Tourist Sites | 3,000,000 | 15% |
This table illustrates a potential allocation of tourism tax revenue for climate change mitigation projects in Iceland. The figures are estimates and can be adjusted based on specific project needs and priorities.
Sustainable Tourism Practices in Iceland
Iceland, a land of breathtaking landscapes and unique wildlife, faces the challenge of balancing its thriving tourism industry with environmental protection. Sustainable tourism practices are crucial to ensuring the long-term health of the island’s ecosystems and the economic well-being of its communities. This approach prioritizes minimizing the negative impacts of tourism while maximizing its benefits for both nature and people.Iceland has actively embraced sustainable tourism initiatives, recognizing the importance of responsible practices for preserving its natural heritage.
These initiatives aim to reduce the environmental footprint of tourism activities while promoting responsible visitor behavior.
Innovative Sustainable Tourism Practices
Iceland has implemented various innovative practices to promote sustainable tourism. These include incentivizing eco-friendly accommodations, supporting local businesses, and promoting responsible wildlife viewing. Many accommodations are now adopting energy-efficient technologies, reducing their carbon footprint and promoting renewable energy sources. Efforts are also focused on minimizing waste, employing water-saving technologies, and utilizing sustainable materials.
Methods for Reducing the Environmental Footprint
Several methods are employed to reduce the environmental footprint of tourism activities. One crucial approach is promoting responsible transportation options. Encouraging the use of public transport, cycling, or walking within destinations can significantly reduce reliance on private vehicles. This strategy also fosters a deeper appreciation of the local environment and culture. Furthermore, promoting responsible waste management and minimizing plastic use are essential elements of reducing the environmental impact.
Iceland’s tourism tax debate is definitely heating up, with concerns about its impact on the environment. Sustainable tourism is key, and I’ve been thinking about how experiences like those offered by inn of the five graces celestial glamping expeditions could help balance the need for revenue with eco-conscious travel. Ultimately, the goal is to support Iceland’s beauty while minimizing the negative effects of mass tourism.
Importance of Responsible Tourism Behavior
Responsible tourism behavior plays a vital role in achieving sustainability goals. Visitors are encouraged to respect local cultures, customs, and traditions. This includes being mindful of noise levels, wildlife interactions, and environmental regulations. Visitors should prioritize responsible consumption, opting for locally sourced food and supporting locally owned businesses. Respecting the fragile ecosystems is paramount.
Iceland’s tourism tax is a hot topic, often linked to the country’s commitment to combating climate change. While the tax itself is designed to mitigate the environmental impact of tourism, it’s not without its critics. For a different kind of winter wonderland experience, consider the glass igloo northern lights tours in Finland. These unique accommodations offer breathtaking views of the aurora borealis, a great alternative for experiencing the magic of the north while reducing your carbon footprint.
Ultimately, Iceland’s tourism tax debate reflects the ongoing global discussion of how to balance economic growth with environmental responsibility. glass igloo northern lights in finland could be a great alternative to consider.
Benefits of Sustainable Tourism Practices
Sustainable tourism practices offer numerous benefits. Firstly, it protects the natural beauty and biodiversity of Iceland. Secondly, it supports the local economy by creating jobs and revenue for local businesses and communities. By supporting local enterprises, tourists directly contribute to the preservation of local crafts, traditions, and cultural heritage. Furthermore, sustainable practices contribute to the long-term viability of the tourism sector, ensuring its continued success for generations to come.
Actions Tourists Can Take to Minimize Environmental Impact
- Choose eco-friendly accommodations: Look for accommodations that prioritize sustainability, such as hotels using renewable energy sources or those committed to reducing their environmental footprint. This includes considering accommodations with a strong environmental policy, such as those employing water-saving technologies and minimizing waste.
- Reduce your carbon footprint: Opt for public transportation, walking, or cycling whenever possible. Minimize air travel whenever possible. Consider the environmental impact of your travel choices. Avoid using single-use plastics. Choose products with sustainable packaging and support companies with sustainable practices.
- Respect wildlife: Maintain a safe distance from wildlife, avoid feeding them, and adhere to any regulations or guidelines set by local authorities. Support initiatives aimed at protecting wildlife habitats. Engage in wildlife viewing responsibly, following guidelines and minimizing disturbance.
- Support local businesses: Choose locally owned restaurants, shops, and tour operators. This supports local economies and helps preserve cultural heritage. Support businesses that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices. Buy souvenirs from local artisans.
- Minimize waste: Reduce your consumption of single-use plastics, carry reusable bags, water bottles, and utensils. Dispose of waste responsibly and recycle when possible. Avoid unnecessary packaging.
The Future of Icelandic Tourism in the Context of Climate Change
Iceland’s stunning landscapes, rich culture, and unique experiences have made it a popular tourist destination. However, the accelerating impacts of climate change pose significant challenges to the future of this vital industry. Adapting to these changes will require a multifaceted approach involving both innovative solutions and a heightened awareness of the issues.Iceland’s tourism sector must proactively address the evolving climate landscape to ensure long-term sustainability and resilience.
This involves not only mitigating the sector’s own environmental footprint but also educating tourists about the impacts of climate change on the island’s fragile ecosystems. This proactive stance will help preserve the very experiences that draw visitors to Iceland in the first place.
Potential Evolution of Iceland’s Tourism Industry
The tourism industry in Iceland is expected to continue its growth trajectory, but its form will likely evolve. Rising sea levels, glacial melt, and extreme weather events will impact the accessibility and beauty of iconic locations. For example, some coastal areas might become inaccessible due to erosion or flooding, requiring the development of alternative tourist routes. This might involve exploring new destinations within Iceland or promoting destinations less affected by climate change.
Potential Adaptations and Innovations in the Tourism Sector
The tourism sector will need to embrace innovative approaches to minimize its environmental footprint. Sustainable transportation options, like electric vehicles and eco-friendly boat tours, will become increasingly important. Furthermore, businesses will need to focus on creating more sustainable accommodations and visitor experiences that minimize resource consumption. For example, eco-lodges and glamping sites are already emerging as more sustainable alternatives to traditional hotels.
Importance of Educating Tourists about Climate Change Impacts
Educating tourists about the environmental impacts of climate change is crucial. This involves providing clear and accessible information about the effects of tourism on the local ecosystems and the importance of responsible behavior. For example, tourists can be informed about the significance of minimizing their carbon footprint during their visit and respecting the delicate balance of nature. This includes providing information about sustainable practices and encouraging responsible consumption.
Role of Tourism Businesses in Promoting Sustainable Practices
Tourism businesses play a pivotal role in fostering sustainable tourism. They can implement environmentally friendly practices in their operations, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing water and energy consumption, and implementing waste management strategies. For example, many businesses are now adopting sustainable practices such as using reusable materials, minimizing single-use plastics, and implementing water conservation measures. This will help minimize their environmental footprint and create a more sustainable visitor experience.
Potential Partnerships Between Tourism Businesses and Environmental Organizations
Collaboration between tourism businesses and environmental organizations is essential for achieving sustainable tourism goals. This can involve joint initiatives for conservation projects, education programs, and the development of sustainable tourism strategies. For example, organizations can work together to create educational programs for tourists, implement sustainable practices in hotels and tour operations, and engage in conservation efforts like reforestation or coastal restoration projects.
The following table Artikels potential areas of collaboration:
| Tourism Business | Environmental Organization | Potential Collaboration |
|---|---|---|
| Accommodation providers | Conservation groups | Joint conservation initiatives, educational programs for guests |
| Tour operators | Glacier protection organizations | Sustainable tour routes, promoting responsible glacier viewing |
| Restaurants | Sustainable food organizations | Promoting local, seasonal food, reducing food waste |
| Transportation providers | Renewable energy organizations | Adoption of electric vehicles, promoting sustainable transport options |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Iceland tourism tax climate change presents a multifaceted challenge. The current tourism tax system, combined with the urgency of climate change, requires a comprehensive approach to sustainability. By incorporating tourism taxes into climate mitigation efforts, Iceland can safeguard its natural beauty for future generations while continuing to benefit from its thriving tourism sector. The future of Icelandic tourism depends on the adoption of sustainable practices, the education of tourists, and innovative collaborations between tourism businesses and environmental organizations.
The path to sustainable tourism in Iceland is achievable, and it requires a collective effort.

Leave a Reply