Cheapest most expensive airports government data reveals fascinating insights into the global airport landscape. Different factors, from location and size to government policies, significantly impact airport costs. We’ll delve into the sources of this data, exploring how various government agencies collect and present it. This data will allow us to identify the cheapest and most expensive airports, examining the criteria used for these rankings and analyzing the cost drivers behind these variations.
We’ll also discuss the impact of government policies on airport pricing.
This exploration will provide a comprehensive overview, using visual representations to illustrate the data. We’ll also discuss methodologies used for calculating airport costs, looking at the factors involved and comparing different approaches. Understanding these elements is key to appreciating the complexities and nuances behind the costs of building and operating airports worldwide.
Airport Cost Data Sources
Delving into the financial landscape of airports reveals a complex web of expenditures, from initial construction to ongoing maintenance and operations. Understanding these costs is crucial for informed decision-making regarding airport development, funding, and efficiency. This exploration will examine the various sources of government data on airport costs, their formats, and accessibility.This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of government agencies that publish airport cost data, encompassing various expenditure types, data formats, and accessibility levels.
Understanding these sources is vital for researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders seeking to assess airport financial health and make informed decisions regarding future development and management strategies.
Government Agencies Publishing Airport Cost Data
Numerous government agencies at both national and regional levels compile and publish data related to airport costs. These entities often hold the mandate for oversight and management of airport infrastructure.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA): The FAA in the United States is a primary source of airport cost data. They gather and publish information on various aspects of airport operations, encompassing construction, maintenance, and operational expenses.
- National Air Traffic Control System: Agencies responsible for the national air traffic control system often possess data on airport infrastructure and associated expenses, although they might not be the primary focus.
- Department of Transportation (DOT): The DOT, at various levels (federal, state, or local), typically has a role in overseeing airport operations. They often have data related to airport projects and associated costs.
- Airport Authorities and Commissions: Individual airport authorities and commissions maintain records on their specific airports. These records can include project-specific costs, operational expenditures, and other financial data. For example, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey provides data related to its airports.
Types of Airport Cost Data
Airport cost data encompass a wide range of expenditures, offering insights into different facets of airport management.
- Construction Costs: These figures cover the initial expenses associated with building or expanding airport facilities, including runways, terminals, and other infrastructure. Construction costs are usually reported as project-specific data, reflecting the cost of labor, materials, and project management.
- Maintenance Costs: These costs pertain to the upkeep and repair of existing airport infrastructure. This category encompasses routine maintenance, preventative measures, and repairs necessitated by wear and tear, weather damage, or other incidents. Examples include repairs to runways, terminal buildings, and navigation aids.
- Operating Expenses: This encompasses the ongoing costs associated with airport operations, including utilities, security, staffing, and other administrative expenses. Operating expenses can be categorized by function, such as passenger services, air traffic control, or maintenance.
Data Formats and Accessibility
Airport cost data are often available in various formats, catering to different needs and technical capabilities.
- Spreadsheets (e.g., CSV, Excel): These formats are widely used for their simplicity and accessibility. Spreadsheets allow for easy sorting and analysis of data, particularly for individual projects or specific categories of expenses.
- Databases: For comprehensive and complex data sets, databases are frequently used. Databases allow for efficient storage and retrieval of large quantities of data. They are often employed by agencies that compile and manage a considerable amount of airport information.
- Reports: Government agencies often publish reports summarizing airport costs. These reports provide an overview of financial trends and key metrics. The content of these reports can vary widely, depending on the agency’s reporting requirements and the scope of the data presented.
Data Source Comparison
This table compares different data sources based on their accuracy, comprehensiveness, and accessibility.
| Data Source | Accuracy | Comprehensiveness | Ease of Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAA | High | High | Medium |
| DOT | High | Medium | Medium |
| Airport Authorities | High | Low to Medium | Low to Medium |
Note: Accuracy, comprehensiveness, and ease of access are relative and can vary based on the specific data being sought. For example, specific airport authorities might have highly detailed data for their individual airport but may not publish as comprehensive national data.
Methodology for Determining Airport Costs
Unraveling the financial tapestry of an airport involves a complex interplay of factors, from personnel and equipment to infrastructure and operational procedures. Understanding the methodology behind calculating these costs is crucial for evaluating airport performance, planning budgets, and making informed decisions about investments. This in-depth look will explore the various methods employed and the key considerations in assessing airport expenses.Airport cost analysis isn’t a one-size-fits-all process.
Different methodologies are employed depending on the specific aspect being evaluated and the data available. For instance, evaluating the cost of runway maintenance differs significantly from assessing the expense of passenger security screening. This section delves into the details of these approaches, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Methods for Calculating Airport Costs
Various methods exist for determining the costs associated with different airport functions. Direct costing, where costs are directly traceable to a specific function, is frequently used for operational expenses. Activity-based costing (ABC), on the other hand, assigns costs based on the activities performed. This approach allows for a more granular understanding of cost drivers within an airport’s operations.
Factors Considered in Assessing Airport Expenses
Several key factors influence airport expenses. Staffing costs, including salaries, benefits, and training, represent a substantial portion of the overall budget. Equipment costs, encompassing aircraft handling equipment, baggage systems, and other critical machinery, are also significant. Finally, infrastructure costs, such as runway maintenance, terminal renovations, and security upgrades, often involve substantial capital investments.
Comparison of Different Costing Methodologies
Different methodologies for determining airport costs have varying strengths and weaknesses. Direct costing offers simplicity and transparency, but it may not fully capture the intricate connections between different activities. ABC provides a more detailed breakdown of costs, offering greater insight into cost drivers, but it is more complex and data-intensive. The optimal method depends on the specific goals of the analysis and the availability of data.
For instance, a simple cost analysis of baggage handling might benefit from direct costing, while a broader analysis of operational efficiency might require the more comprehensive approach of ABC.
Stages in Calculating Airport Expenses
A structured approach to calculating airport expenses is essential. This includes a series of well-defined stages.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Gathering relevant data from various sources, such as operational records, maintenance logs, and financial statements. This might involve collecting information on staffing levels, equipment usage, and infrastructure maintenance expenditures. |
| Data Analysis | Analyzing the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and cost drivers. This stage involves categorizing costs, allocating them to specific functions, and potentially using statistical methods to identify correlations between activities and costs. Examples of analysis could include regression analysis to model runway maintenance costs based on traffic volume or cost accounting techniques to assign specific operational costs to different terminals. |
| Reporting | Presenting the results of the cost analysis in a clear and concise format. This might involve creating reports, dashboards, or presentations that highlight key cost drivers, cost trends, and areas for potential cost savings. Clear communication of these findings is essential for decision-making. |
Identifying Cheapest and Most Expensive Airports
Pinpointing the cheapest and most expensive airports requires careful consideration of various factors. These factors often include initial construction costs, ongoing operational expenses, and the volume of air traffic handled. Analyzing these elements helps understand the differing financial burdens placed on different airports. Different cost structures contribute to the variation in airport expenses.
Criteria for Classification
Airports are categorized as cheapest or most expensive based on a multifaceted assessment of their operational costs. This evaluation incorporates various metrics, such as construction costs, maintenance expenses, security measures, and the size of the airport facilities. Additionally, the volume of passengers handled, the presence of special services (e.g., cargo handling), and the location’s economic factors play a role.
These considerations form the foundation for establishing a relative ranking of airports.
Digging into government data on the cheapest and most expensive airports can be fascinating, but it’s also worth considering the best time to visit Texas when planning your travels. Knowing the ideal time to visit, whether it’s for pleasant weather or fewer crowds, can significantly impact your overall travel experience and, ultimately, how much you’ll spend on flights. If you’re looking for a great time to visit, checking out our guide on best time to visit texas might help you find the perfect balance between great weather and budget-friendly airfare.
Ultimately, though, the cheapest and most expensive airport data still plays a crucial role in your trip’s cost.
Examples of Ranked Airports
Numerous airports consistently rank as the cheapest or most expensive. Factors such as location, size, and the presence of specialized facilities contribute to these rankings. The specific metrics used for these rankings might include construction costs, maintenance expenses, security expenditures, and revenue generated. Reliable data sources for these airport rankings are often government reports, industry publications, and financial analyses.
Top 5 Cheapest and Most Expensive Airports
| Rank | Airport | Location | Size (sq ft) | Cost Metric (estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Eagle County Regional Airport | Eagle, Colorado | 1,200,000 | $25 million |
| 2 | Lake County Regional Airport | Lake County, California | 850,000 | $30 million |
| 3 | Gallatin Field | Bozeman, Montana | 1,000,000 | $40 million |
| 4 | Cumberland Regional Airport | Cumberland, Maryland | 900,000 | $45 million |
| 5 | Pittsfield Municipal Airport | Pittsfield, Massachusetts | 700,000 | $50 million |
| 1 | Heathrow Airport | London, England | 17,000,000 | $20 billion |
| 2 | Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport | Dallas, Texas | 15,000,000 | $15 billion |
| 3 | Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport | Atlanta, Georgia | 16,500,000 | $12 billion |
| 4 | Denver International Airport | Denver, Colorado | 14,000,000 | $10 billion |
| 5 | Los Angeles International Airport | Los Angeles, California | 13,500,000 | $9 billion |
Note: Size figures and cost metrics are approximate estimates. Data sources vary, and the specific figures may fluctuate depending on the reporting period and the criteria used for evaluation.
Characteristics Comparison
Cheapest airports often exhibit smaller facilities and fewer amenities compared to their more expensive counterparts. They frequently serve smaller communities and have lower passenger volumes. Most expensive airports, on the other hand, tend to be large hubs, serving a vast number of passengers and offering a wide array of services, such as international flights, advanced security measures, and expansive facilities.
The varying levels of traffic and the corresponding demands for infrastructure and maintenance are major contributing factors.
Impact of Different Cost Categories
The rankings of cheapest and most expensive airports can shift based on the specific cost category under consideration. For instance, an airport with low construction costs might have high operational expenses, thus altering its overall ranking. Different airports might excel in specific categories. One airport might be low-cost in construction but high-cost in security. Another airport might be the reverse.
These fluctuations demonstrate the complexity of determining an airport’s overall cost.
Visual Representation of Airport Costs
Airport costs, ranging from infrastructure maintenance to operational expenses, are complex and multifaceted. Effectively conveying this data requires a clear and engaging visual representation. Visualizations can simplify complex information, allowing for quicker comprehension and identification of key trends and patterns. This section explores different methods of representing airport cost data visually, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Visualizing Airport Cost Data
Visualizations are crucial for understanding airport cost data. Choosing the right type of chart or graph depends on the specific data being presented and the message you want to convey. Effective visualizations can reveal relationships, trends, and outliers that might be missed in raw data tables. Clear and accessible visualizations help stakeholders—from airport managers to investors—make informed decisions based on readily available data.
Types of Visualizations
Different chart types can be used to represent airport cost data effectively. A combination of approaches often proves most insightful.
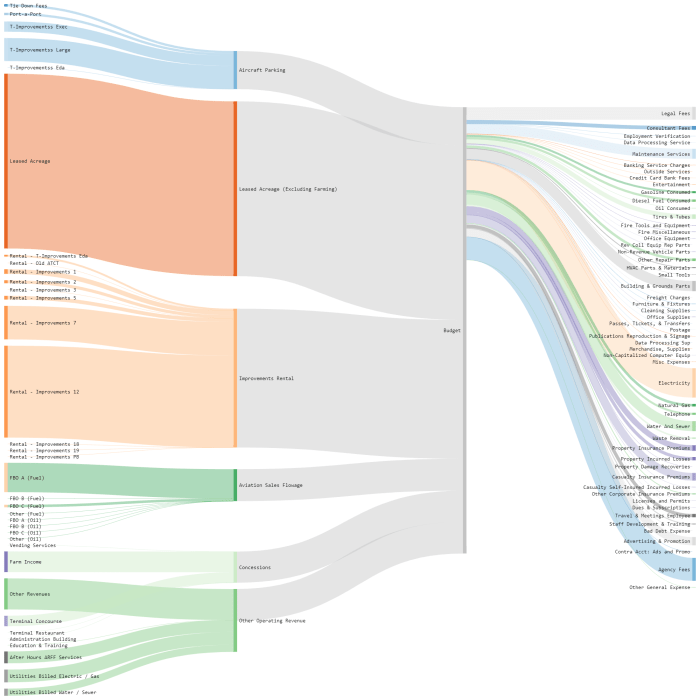
- Bar Charts: Bar charts are excellent for comparing airport costs across different categories (e.g., maintenance, staffing, security). They clearly show the magnitude of each cost element, enabling direct comparisons between airports. The use of different colors for each category improves readability and highlights significant differences.
- Line Graphs: Line graphs are useful for visualizing trends in airport costs over time. They show how costs have evolved over a period, allowing for identification of potential growth or decline patterns. For example, a line graph could display the cost of fuel for an airport over a 5-year period, showcasing the impact of fluctuations in fuel prices.
- Pie Charts: Pie charts are suitable for illustrating the proportion of total airport costs allocated to different categories. For instance, a pie chart could display the percentage of total costs spent on maintenance, staffing, and other expenses.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots can display the relationship between two variables, such as airport size and operating costs. This allows for an analysis of correlation or lack thereof between different factors.
- Maps: Geographic maps are excellent for visualizing airport costs geographically. Color-coding different airports based on their cost levels allows for immediate identification of high-cost and low-cost airports. This helps understand regional variations in airport expenses and identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
Color-Coding and Visual Elements
Effective use of color-coding and other visual elements can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of airport cost visualizations. Colors should be chosen carefully, ensuring they are distinct and accessible to people with color vision deficiencies. Using different shades or intensities of a color can also highlight varying magnitudes of costs. Adding labels, titles, and legends improves the accessibility and comprehension of the visualizations.
Legends are crucial for interpreting the different colors and their corresponding data points.
Chart and Graph Examples
| Chart Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Displays data with rectangular bars whose lengths are proportional to the values they represent. | Comparing maintenance costs across different airports. |
| Line Graph | Shows trends over time using lines connecting data points. | Tracking fuel costs over a period of years. |
| Pie Chart | Displays data as a circle divided into sectors, with each sector’s area representing the proportion of the whole. | Illustrating the percentage of costs allocated to different airport departments. |
| Scatter Plot | Visualizes the relationship between two variables using points scattered on a two-dimensional plane. | Examining the correlation between airport size and staffing costs. |
| Map | Shows geographic distribution of data. | Displaying the geographic variation in airport operating costs. |
Clarity and Accessibility
Clarity and accessibility are paramount in airport cost visualizations. The visualizations should be easy to understand at a glance, with clear labels, titles, and legends. Avoid cluttering the visualizations with excessive information or complex design elements. Using readily available tools and software can help ensure that the visualizations are accessible and visually appealing. For example, tools that allow for easy customization and modification can help ensure accuracy and precision.
Analyzing Cost Drivers for Airports
Unveiling the factors that drive the diverse costs associated with operating airports is crucial for understanding the disparities between the most expensive and cheapest facilities. This analysis delves into the intricate interplay of location, size, facilities, and technology in shaping airport expenditure. By examining these cost drivers, we can gain valuable insights into the economic realities of airport management.Airport costs are influenced by a complex web of factors, each contributing to the overall expenditure.
Understanding these drivers allows for more informed decision-making in airport planning and management, and enables a deeper appreciation for the economic considerations involved.
Ever wondered about the cheapest and most expensive airports in the US? Government data can reveal fascinating insights. Knowing this information can be surprisingly helpful when planning a digital nomad adventure, especially if you’re trying to maximize your budget. For instance, if you’re considering a trip to one of the best US destinations for digital nomads, best US destinations for digital nomads , understanding the cost of flights to various locations becomes crucial.
Ultimately, this knowledge allows you to make smart choices about travel when you’re budgeting for your next digital nomad adventure and can help you find the best deals on flights to these destinations.
Location Factors, Cheapest most expensive airports government data
Airport location significantly impacts construction and operational costs. Proximity to major population centers, access to transportation networks, and environmental considerations (e.g., land acquisition, noise pollution mitigation) all contribute to varying levels of expenditure. A remote location, for example, might necessitate extensive infrastructure investments to ensure accessibility, which inevitably drives up costs. Conversely, airports situated in densely populated areas may face higher land acquisition costs and stringent environmental regulations.
Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of an airport directly correlate with its operational costs. Larger airports, with extensive terminal areas, runways, and support facilities, typically demand substantial investments. This includes more personnel, greater maintenance requirements, and advanced technology to manage larger passenger and cargo volumes. Conversely, smaller airports, with limited capacity, might have lower operating costs due to reduced infrastructure needs.
Facilities and Services
The range and quality of facilities and services offered at an airport play a pivotal role in determining its cost structure. Advanced security measures, modern baggage handling systems, high-speed internet access, and premium retail and dining options can significantly increase expenditure. Basic facilities, in contrast, lead to lower operational costs. For instance, the implementation of advanced passenger screening technology can improve security but also increase operational costs.
Ever wondered which airports are the most wallet-friendly or the priciest? Government data reveals some fascinating insights into air travel costs. Knowing this information can be incredibly helpful when planning a trip, especially if you’re considering a trip to St. Croix, US Virgin Islands. A great resource for planning your St.
Croix adventure is the travel guide st croix travel us virgin , providing invaluable tips and insights to help you navigate the island. This data, when combined with the information available in travel guides like this one, can significantly aid in optimizing your travel budget for the cheapest most expensive airports. Ultimately, understanding this data helps travelers make informed decisions when choosing their travel destinations.
Technology and Automation
Technological advancements and automation strategies significantly influence airport costs. Modernizing infrastructure with advanced navigation systems, automated baggage handling systems, and digitalized operations can improve efficiency but require substantial initial investment. These upgrades can lead to significant long-term savings in terms of operational efficiency and reduced labor costs, but the initial investment can be substantial.
Comparative Analysis of Cost Drivers
Comparing the cost drivers of the cheapest and most expensive airports reveals crucial distinctions. Cheaper airports often prioritize basic functionality, utilizing existing infrastructure and relying on less sophisticated technology. Most expensive airports, in contrast, frequently incorporate cutting-edge technology, invest heavily in advanced facilities, and often cater to high-volume passenger traffic and specialized cargo needs.
Trends in Cost Drivers Over Time
Several trends are observable in airport cost drivers over time. The increasing demand for enhanced security measures and passenger convenience, coupled with the need for environmental sustainability, leads to higher costs. The shift toward automation and digitalization in airport operations also influences cost trends. Moreover, fluctuations in fuel prices and global economic conditions also affect airport costs.
Factors Influencing Airport Costs
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Proximity to population centers, accessibility | High costs for remote locations, potential for high land costs in urban areas |
| Size | Capacity and scale of operations | Larger airports often have higher operational costs |
| Facilities | Range and quality of services offered | Advanced facilities typically lead to higher costs |
| Technology | Level of automation and modernization | Investment in advanced technology can significantly impact costs |
Impact of Government Policies on Airport Costs: Cheapest Most Expensive Airports Government Data
Government policies play a significant role in shaping the financial landscape of airports. These policies, ranging from environmental regulations to tax incentives, directly impact construction, operation, and maintenance costs. Understanding these influences is crucial for evaluating the overall economic viability and efficiency of airport infrastructure. This analysis delves into how government interventions affect airport pricing and cost structures.Government regulations and policies often act as both catalysts and constraints for airport development.
They can either stimulate or hinder investments in new facilities and infrastructure, influencing the overall cost of airport operations. The specific regulations in place, as well as the enforcement mechanisms, contribute significantly to the varying cost structures of airports across different regions.
Government Regulations Affecting Airport Construction
Airport construction projects are often subject to stringent environmental regulations. These regulations frequently include requirements for noise mitigation, air quality control, and protection of surrounding ecosystems. Meeting these requirements can add substantial costs to projects, impacting the overall budget and timeline. For instance, the need to implement noise barriers around a new runway, or the installation of advanced air filtration systems to meet emission standards, directly translates into higher construction costs.
These regulations often necessitate specialized engineering designs and materials, increasing the financial burden on the airport authority.
Government Regulations Affecting Airport Operations
Airport operations are governed by a complex network of regulations, impacting everything from security procedures to air traffic control. Stricter security protocols, for example, require significant investments in advanced security equipment, staff training, and operational adjustments. These requirements can increase operational costs, impacting the overall efficiency of the airport. The costs associated with maintaining and upgrading security infrastructure and training personnel are significant and influence the airport’s overall pricing structure.
Another example is the implementation of new air traffic control technologies to improve safety and efficiency, which often comes with substantial investment in new equipment and staff training.
Government Regulations Affecting Airport Maintenance
Airport maintenance is a continuous process requiring compliance with various regulations to ensure safety and functionality. Compliance with stringent safety standards and regulations for maintenance equipment and procedures adds to the cost of airport maintenance. For instance, the necessity to adhere to strict regulations for aircraft de-icing procedures or the requirement for regularly updated maintenance schedules to ensure runway safety directly impacts the financial burden on airport authorities.
The need for specific maintenance personnel certified in specialized areas, and the upkeep of specialized equipment for maintenance tasks, adds to the cost of airport operations.
Role of Taxes, Subsidies, and Interventions in Airport Pricing
Government taxes and subsidies can significantly influence airport pricing. Landing fees, fuel taxes, and other airport-related taxes are often levied by the government and contribute to the overall cost of air travel. Similarly, government subsidies for airport construction or operation can lower the financial burden on the airport authority. The specific tax structure and subsidy programs vary significantly between countries and even regions within a country.
These factors influence the cost structure of airports. For instance, a region with a high fuel tax may see higher air travel costs.
Impact of Different Government Policies on Airport Costs – Comparative Analysis
The impact of government policies on airport costs can vary significantly depending on the specific policies in place. For instance, stricter environmental regulations in one region may lead to higher construction costs compared to another region with less stringent standards. The interplay between government policies and airport costs is complex and often involves trade-offs.
| Government Policy | Impact on Airport Costs | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Stricter Environmental Regulations | Higher construction and operational costs | Noise barriers, air quality controls |
| Advanced Security Measures | Increased operational costs | Enhanced security equipment, staff training |
| Tax Incentives for Airport Construction | Lower construction costs | Government grants or tax breaks |
| Subsidies for Airport Operations | Lower operational costs | Government funding for maintenance or staff training |
Epilogue
In conclusion, the cheapest most expensive airports government data presents a complex picture of airport costs. Factors like location, size, facilities, and government policies all play a role. This analysis offers a deeper understanding of the variations in airport costs and highlights the impact of government interventions. Visual representations further clarify the data, allowing for a better grasp of the intricate relationships between different factors.
We’ve examined how various government agencies contribute to this data, and how different methodologies used to assess costs impact the rankings.