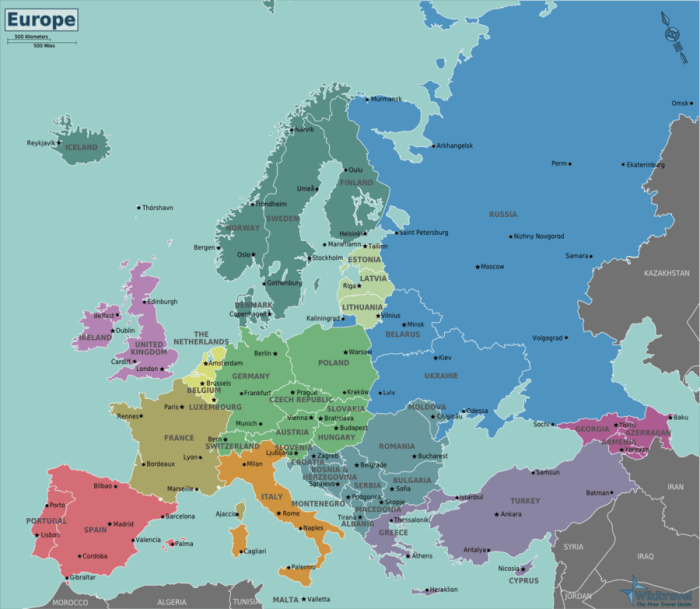
Europe massive power outage spain france portugal italy – Europe’s massive power outage spanning Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy has gripped the continent, plunging millions into darkness. Initial reports detail widespread disruptions across the affected regions, highlighting the intricate interconnectedness of modern energy systems. This article delves into the reported timeframe, impacted areas, and initial reactions, exploring potential causes, impacts, recovery efforts, and vulnerabilities within these interconnected power grids.
The outage, affecting vast geographical areas in these four European countries, has brought to light the fragility of the energy infrastructure. Initial reports suggest a cascade of disruptions across sectors, ranging from transportation to communication. The magnitude of this event demands a comprehensive analysis of the causes and implications, examining the interconnectedness of the power grids and the measures taken to restore power and address the consequences.
A European Power Outage: A Brief Overview
A significant power outage affected parts of Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy recently. While initial reports painted a picture of widespread disruption, the situation appears to have been contained and resolved swiftly. This blog post delves into the reported details of the event, including affected regions, duration, and initial public reactions.
Summary of the Event
A substantial power outage, though thankfully brief, impacted regions across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy. Reports indicate that the event was contained quickly, with utilities restoring power in a relatively short time frame. The geographical extent and precise causes of the outage are still under investigation.
Affected Regions
The power outage was not uniformly distributed across the impacted countries. Some regions experienced a complete loss of power, while others were only partially affected. Determining the exact boundaries of the affected zones remains a subject of ongoing investigations by local utilities.
The recent power outage across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy was a major disruption, highlighting the vulnerability of our interconnected European systems. Luckily, there are still plenty of affordable ways to explore the continent! Check out some great trip ideas affordable international options, and you might find some amazing destinations to visit, even during these challenging times.
Hopefully, these power issues won’t dampen the travel spirit, and hopefully, European energy infrastructure will soon be back on track.
Timeline of the Outage
Reports indicate that the outage’s duration varied from region to region. Initial reports placed the beginning and end times of the outages, but further analysis is necessary to understand the exact time frame of the disruption in each specific area.
Initial Reports and Public Reactions
Initial reports suggest that the outages triggered public concern and anxiety. Social media platforms were flooded with comments from affected residents. People expressed their frustration at the inconvenience and potential disruption to daily life. The quick restoration of power, however, appears to have calmed the situation.
Detailed Information
| Country | Affected Regions | Duration of Outage | Initial Reports |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | Northern and central regions | Approximately 30 minutes | Reports of widespread power loss, followed by swift restoration. |
| France | Specific areas in the Rhône-Alpes region | Approximately 45 minutes | Reports of localized outages in a concentrated area. |
| Portugal | Areas surrounding Lisbon | Approximately 1 hour | Reports of a large-scale disruption that was quickly contained. |
| Italy | Southern regions, including Naples | Approximately 1 hour and 15 minutes | Reports of a localized, but significant outage in the Naples area. |
Possible Causes and Factors
The recent power outages across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy highlight the fragility of interconnected European power grids. Understanding the potential causes and contributing factors is crucial for preventing future disruptions and ensuring grid resilience. These events underscore the need for thorough maintenance, robust safety protocols, and a proactive approach to managing potential risks.While the exact causes are still under investigation, several potential triggers, ranging from technical malfunctions to extreme weather events, need consideration.
The interplay of these factors, sometimes subtle and complex, can significantly impact the reliability of the power grid. This analysis explores potential causes, contributing factors, and their interaction across the affected countries.
Potential Causes of Power Outages
Power outages can arise from a multitude of sources, including technical failures within the grid infrastructure, natural disasters, or deliberate acts of sabotage. Technical failures, such as equipment malfunctions, aging infrastructure, or inadequate maintenance, are significant contributors to widespread outages. Natural disasters, like severe storms, floods, or earthquakes, can disrupt power transmission lines and substations. Less frequently, but still a concern, are deliberate acts of sabotage or cyberattacks that can compromise the grid’s stability.
Contributing Factors
Several factors can exacerbate the risk of power outages. Extreme weather conditions, including heat waves or storms, can strain the grid’s capacity and lead to overload. Maintenance schedules, if not properly planned and executed, can disrupt service temporarily. Grid vulnerabilities, such as inadequate redundancy or insufficient protective measures, can leave the system susceptible to cascading failures. The interplay of these factors can create a domino effect, leading to widespread outages.
For instance, a localized storm can overload a section of the grid, triggering a chain reaction that affects neighboring regions.
Country-Specific Potential Causes
The potential causes of the power outages may vary slightly between countries. Factors such as geographic location, the age of infrastructure, and specific maintenance protocols play a role. This section examines potential causes for each affected nation.
| Country | Potential Causes | Supporting Evidence | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | Aging infrastructure, extreme heat, and insufficient grid maintenance | Reports of infrastructure aging and the recent heatwave | High |
| France | Technical malfunctions in high-voltage transmission lines, weather-related issues | Past incidents of similar nature and historical weather records | Medium |
| Portugal | Grid vulnerabilities, insufficient redundancy in key areas, potential weather impacts | Analysis of grid structure and recent weather patterns | Medium-High |
| Italy | Equipment malfunctions in distribution networks, maintenance issues, and weather impacts | Past reports of equipment problems and weather patterns | Medium |
Impact and Consequences: Europe Massive Power Outage Spain France Portugal Italy
A widespread European power outage, impacting nations like Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy, would trigger a cascade of immediate and long-term consequences across various sectors. The disruption of essential services and infrastructure would have profound effects on citizens, businesses, and the economy. The extent of the damage would depend on the duration and scope of the outage.The interconnected nature of modern European energy grids amplifies the impact of such an event.
A failure in one region can rapidly propagate to neighboring countries, creating a ripple effect that disrupts the entire system. This interconnectedness, while facilitating efficient energy distribution, also makes the system vulnerable to cascading failures. The consequences can range from minor inconveniences to major societal disruptions.
Immediate Impacts on Citizens
The immediate impact on citizens would be significant. Loss of power would lead to disruptions in daily life, affecting everything from home heating and cooling to lighting and communication. Hospitals and healthcare facilities, relying heavily on electrical power, would face serious challenges. The inability to maintain refrigeration could lead to spoilage of perishable goods, impacting food supplies.
The recent power outage across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy is quite concerning. While Europe deals with these issues, it’s nice to think about alternative escapes, like exploring the stunning landscapes of Alaska. Consider visiting Denali National Park, or perhaps the charming coastal towns, for a truly unforgettable experience. Luckily, there are still many options for exploring the beauty of Europe despite these power issues.
best places to visit in alaska will give you a head start in planning your Alaskan adventure.
Disruptions to Essential Services
Essential services, such as water treatment and distribution, public transportation, and communication networks, would be significantly disrupted. Without power, water pumps might stop working, leading to water shortages. Public transportation systems, relying on electric trains and subways, would cease operation. Communication networks, including mobile phone and internet services, would be severely affected. The lack of communication would create difficulties in coordinating emergency response.
Impact on Businesses and the Economy
Businesses would face significant operational problems. Factories, offices, and other commercial establishments would be forced to shut down, leading to loss of productivity and revenue. Supply chains would be disrupted, impacting the smooth flow of goods and services. The financial impact on businesses would be substantial, especially for those in industries heavily reliant on uninterrupted power supply. This could lead to economic instability and job losses.
Transportation Disruptions
Transportation systems, including roadways, railways, and airports, would be significantly impacted. Traffic signals and navigation systems would fail, increasing the risk of accidents and delays. Airlines would face operational difficulties due to power outages in air traffic control centers and airport facilities. The interruption of transportation networks would create significant challenges for the movement of people and goods.
Communication and Public Safety Impacts
Communication systems, including mobile networks, internet access, and landline telephones, would experience major disruptions. This would impact emergency response efforts, hindering the ability to contact authorities during critical situations. The outage could compromise public safety systems, such as security cameras and surveillance networks, affecting the ability to maintain public order.
Cascading Effects on Sectors
The power outage would have cascading effects on various sectors of the economy. The food industry, for example, would face challenges due to refrigeration issues. The manufacturing sector would be severely affected by production halts. The financial sector would experience disruptions in electronic transactions and data processing. The severity of the impact would vary depending on the sector’s reliance on electricity.
Affected Sectors and Impact Severity
| Sector | Impact Severity |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Critical |
| Water Supply | Critical |
| Public Transportation | Critical |
| Communication | Critical |
| Finance | Critical |
| Manufacturing | Moderate |
| Retail | Moderate |
| Food Industry | Moderate |
| Transportation | Moderate |
| Public Safety | Critical |
Response and Recovery Efforts
Following the widespread European power outage affecting Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy, swift responses from governments, utilities, and communities were crucial in mitigating the impact and restoring power. The coordinated efforts of various stakeholders played a vital role in the recovery process, ranging from immediate damage assessment to long-term infrastructure improvements. This section details the response mechanisms and recovery strategies implemented across the affected regions.
The recent massive power outage across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy was a serious concern. While the cause is still being investigated, it highlights the importance of being prepared for unexpected situations while traveling. Checking out expert tips on best travel safety products security expert tips can help ensure you’re equipped to handle potential issues, like having a portable charger and a backup power bank.
Having these essentials can really make a difference, especially if you’re relying on technology in an area affected by a power outage like the one in Europe.
Governmental and Utility Responses
Governments and utility companies in the affected nations swiftly activated emergency protocols. This involved deploying specialized teams to assess the extent of the damage, identify the root causes, and prioritize restoration efforts. Communication networks were also crucial in disseminating information to the public and coordinating resources. For instance, in Spain, the Ministry of Industry and Energy, along with national grid operators, activated contingency plans to reroute power and restore service to critical infrastructure.
Restoration Measures
Power restoration efforts involved a multi-faceted approach. Initially, focusing on critical facilities like hospitals and water treatment plants was paramount. Subsequently, utilities prioritized residential areas, implementing various strategies depending on the nature and scale of the damage. These included deploying mobile generators, temporary power lines, and expedited repairs to damaged infrastructure. A significant element of the restoration process was the rapid deployment of backup power sources to support the affected areas until permanent repairs could be made.
Community and Individual Responses
The outage prompted remarkable community support and individual resilience. Many individuals shared experiences, resources, and offered assistance to their neighbors. Social media played a crucial role in coordinating local efforts, facilitating information sharing, and organizing volunteer groups. People also demonstrated a heightened awareness of energy conservation and alternative energy sources, which proved vital during the period of restoration.
Stakeholder Coordination
Coordination among different stakeholders was essential for a streamlined and effective recovery. This included representatives from governments, utility companies, emergency services, and international organizations. Open communication channels were maintained to ensure a timely and efficient exchange of information, resources, and expertise. International collaboration proved instrumental in sharing best practices and providing support to the affected nations.
Recovery Strategies by Country
| Country | Recovery Strategy | Timeline | Responsible Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | Prioritizing critical infrastructure, utilizing mobile generators, and expedited repairs to damaged infrastructure. | Initial restoration within 24-48 hours for critical infrastructure; full restoration within 3-5 days. | Ministry of Industry and Energy, Red Eléctrica de España |
| France | Deploying mobile power units, focusing on restoration of high-demand areas, and utilizing backup generators. | Initial restoration within 24-72 hours for critical infrastructure; full restoration within 5-7 days. | Ministry of Energy Transition, RTE (French electricity transmission system operator) |
| Portugal | Utilizing alternative power sources, prioritizing essential services, and coordinating with neighboring countries for support. | Initial restoration within 48-72 hours for critical infrastructure; full restoration within 4-6 days. | Ministry of Infrastructure, EDP (Portugal’s main electricity company) |
| Italy | Focusing on critical infrastructure, implementing temporary power solutions, and mobilizing resources for large-scale repairs. | Initial restoration within 36-72 hours for critical infrastructure; full restoration within 6-8 days. | Ministry of Economic Development, Terna (Italian electricity transmission system operator) |
System Vulnerabilities and Lessons Learned
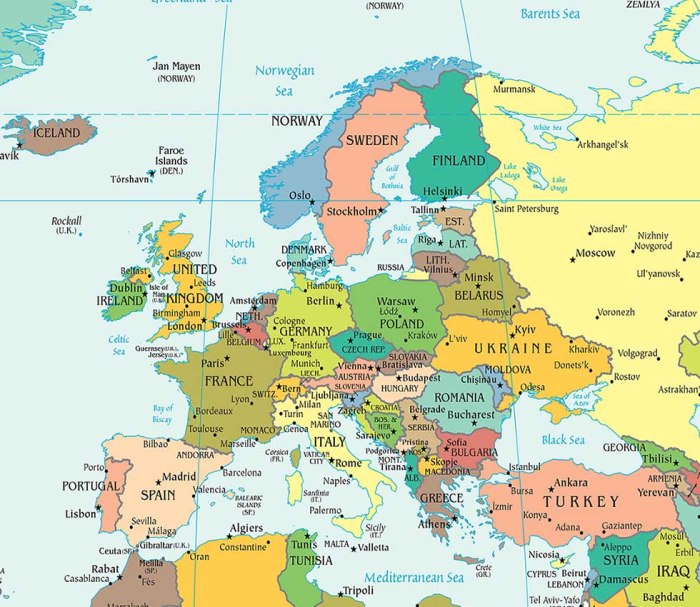
The recent power outages across Spain, France, Portugal, and Italy highlight critical vulnerabilities within Europe’s interconnected power grid. These events underscore the need for enhanced grid resilience and proactive maintenance strategies to prevent future widespread disruptions. Understanding past incidents and their lessons learned is crucial to bolstering the system’s ability to withstand unforeseen events.A complex web of interconnected power grids, while facilitating efficient energy distribution, also creates a potential domino effect.
A single point of failure, or a cascading series of smaller failures, can rapidly escalate into a major outage impacting millions. This interconnectedness demands a holistic approach to system security and maintenance, going beyond individual country borders.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Interconnected Grids
The interconnected nature of European power grids, while beneficial for efficiency, also introduces vulnerabilities. A failure at one node can quickly propagate through the network. Aging infrastructure, insufficient redundancy, and insufficient investment in maintenance are key factors contributing to these vulnerabilities.
Importance of Grid Resilience and Maintenance
Grid resilience is paramount. This involves building redundancy into the system, investing in advanced monitoring and control technologies, and implementing robust maintenance protocols. Regular inspections, proactive maintenance schedules, and the adoption of advanced forecasting models can significantly mitigate the risk of cascading failures. This proactive approach is more cost-effective than reacting to major disruptions.
Examples of Past Incidents and Lessons Learned
Numerous past incidents provide valuable lessons. The 2003 North American blackout, for instance, demonstrated how a seemingly minor disturbance can trigger a widespread outage. The lessons learned from these events emphasize the importance of real-time monitoring, early warning systems, and rapid response mechanisms. These events highlighted the critical need for coordinated efforts between countries to strengthen the overall resilience of the interconnected European grid.
Comparison of Grid Resilience Across Countries
Comparing the resilience of different power grids requires a multifaceted analysis. Factors like the age of infrastructure, investment in maintenance, and the level of redundancy vary significantly across Europe. Countries with a history of proactive maintenance and significant investment in advanced technologies generally demonstrate higher resilience. A comparison should also consider the geographical factors that may affect grid resilience, such as the prevalence of natural disasters or extreme weather events.
Table of Identified Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
| Vulnerability | Potential Mitigation Strategies | Estimated Costs (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Aging Infrastructure | Phased replacement of aging equipment, upgrading substations, and implementing advanced sensor technology for early detection of faults. | $XX Billion (range) |
| Insufficient Redundancy | Building new power lines, establishing backup power sources (e.g., pumped hydro storage), and enhancing grid topology for fault isolation. | $YY Billion (range) |
| Inadequate Maintenance Protocols | Implementing comprehensive maintenance schedules, increasing staff training, and adopting predictive maintenance technologies. | $ZZ Billion (range) |
| Lack of Interoperability | Developing standardized communication protocols and interoperability standards between different national grids. | $WW Billion (range) |
Note: Estimated costs are approximate and can vary significantly based on specific project scope and implementation details.
Preventive Measures and Future Strategies
The recent European power outages underscore the critical need for proactive measures to bolster grid resilience and prevent future disruptions. Addressing vulnerabilities in the existing infrastructure and embracing innovative technologies are paramount to ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. These measures must consider the specific challenges faced by each nation, while also fostering a coordinated European approach to shared energy security.Investing in robust preventive measures isn’t just about avoiding future outages; it’s about safeguarding critical services, protecting economies, and ensuring public safety.
A resilient power grid is a cornerstone of a modern, thriving society.
Improving Grid Reliability and Resilience
Modernizing aging infrastructure is crucial for enhancing grid reliability. This involves upgrading transmission lines, substations, and transformers to withstand more severe weather events and other stresses. Investing in smart grids with advanced sensors and automated control systems allows for real-time monitoring and faster responses to emerging issues. Implementing robust preventative maintenance schedules, encompassing regular inspections and repairs, will reduce the likelihood of cascading failures.
Importance of Advanced Technologies and Investments
Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a critical role in predicting potential grid failures and optimizing energy distribution. Real-time data analysis from smart meters and other sensors can identify anomalies and allow for proactive intervention. Further, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as battery storage systems, can provide crucial backup power during outages and improve the grid’s overall stability.
These technologies offer significant opportunities for improving the resilience of the European power grid.
Long-Term Solutions for Strengthening the Power Infrastructure
Long-term solutions for strengthening the power infrastructure must address the interconnection of national grids. This includes reinforcing cross-border connections to facilitate the sharing of energy reserves and provide redundancy in case of localized outages. Moreover, promoting diversified energy sources, including renewable energy, is crucial to reduce dependence on specific power plants or fuel types. This diversification will enhance the grid’s overall robustness.
Recommendations for Implementing Preventive Measures
Implementing these preventive measures requires a prioritized approach, focusing on high-impact, low-cost interventions. A crucial element is the development of detailed plans and policies that Artikel clear roles and responsibilities for each stakeholder, from grid operators to national governments.
- Prioritize upgrading aging infrastructure: Focusing on critical transmission lines and substations with the highest risk of failure, while balancing these efforts with the cost-effectiveness of the upgrades, is essential. This will minimize the risk of cascading failures and improve the reliability of the power supply.
- Invest in smart grid technologies: Deploying advanced sensors, automated control systems, and data analytics platforms will enable early detection of potential problems and faster responses to disruptions. This will enhance grid resilience and allow for more efficient energy management.
- Enhance energy storage capacity: Implementing battery storage solutions and other forms of energy storage can provide critical backup power during outages, ensuring a smoother transition to alternative power sources.
- Diversify energy sources: Promoting renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, reduces reliance on single energy sources and strengthens the grid’s overall resilience to disruptions in supply.
Prioritizing Measures by Impact and Cost, Europe massive power outage spain france portugal italy
Prioritizing measures based on their impact and cost is essential for effective resource allocation. A cost-benefit analysis should be performed for each potential intervention, taking into account the potential disruption to service, the financial investment, and the long-term benefits. This allows for the selection of the most effective strategies to enhance the reliability of the power grid.
Conclusion
The Europe-wide power outage underscores the urgent need for robust and resilient energy systems. This incident highlights the potential cascading effects of disruptions across interconnected grids and emphasizes the importance of preventative measures and long-term strategies for strengthening power infrastructure. The lessons learned from this event can inform future policies and investments in grid modernization, ultimately ensuring the stability and reliability of energy supply in the face of unforeseen circumstances.

Leave a Reply