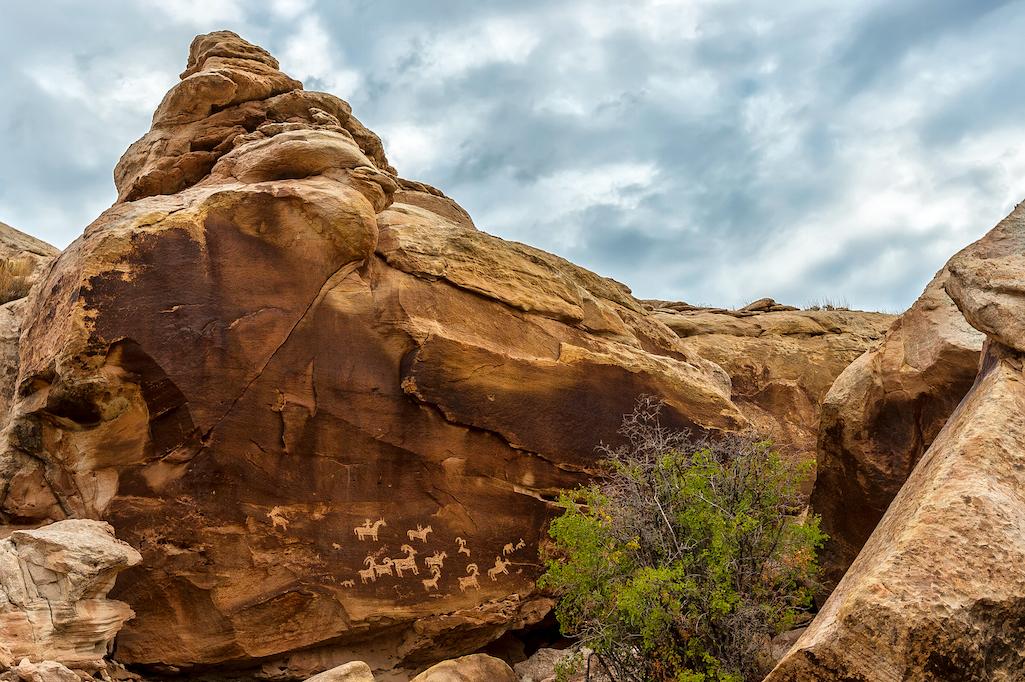
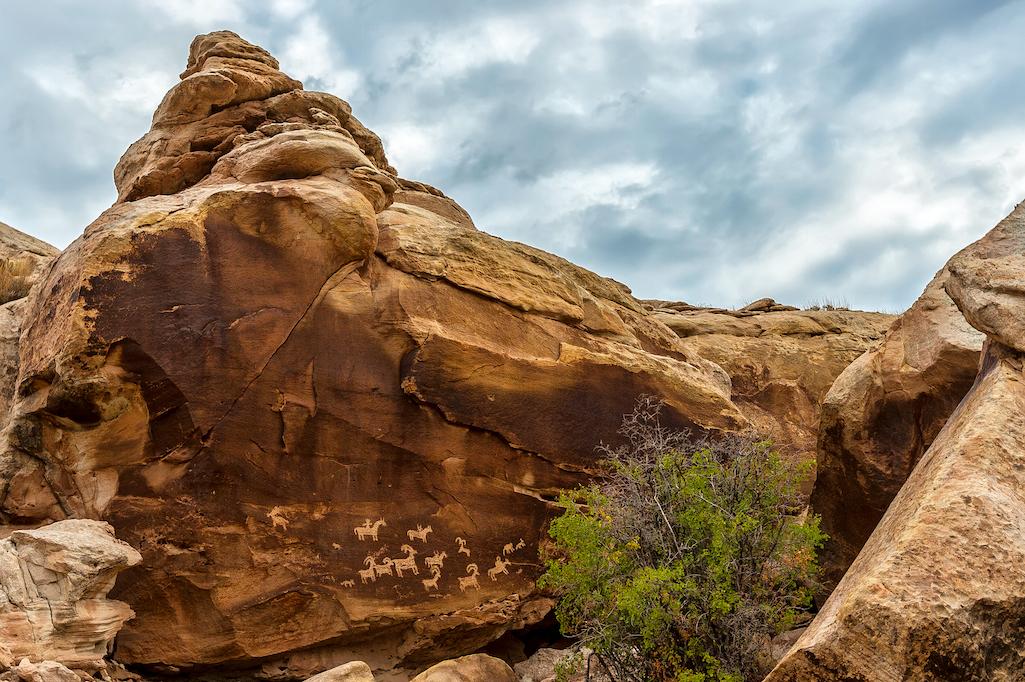
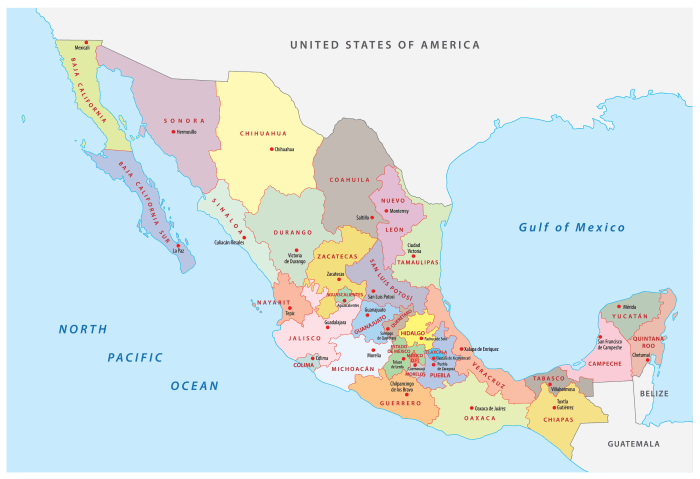
Mexico best national parks – Mexico’s best national parks offer a breathtaking array of landscapes, from towering canyons to vibrant rainforests. This exploration dives deep into the diverse ecosystems, highlighting the unique beauty and significance of these protected areas.
This guide explores the top national parks, comparing their size, location, and climate. We’ll also delve into the fascinating wildlife, activities, and conservation efforts within each park, offering insights into the cultural and historical context, as well as safety precautions for visitors.
Introduction to Mexico’s National Parks

Mexico boasts a stunning array of natural landscapes, from towering volcanoes to vibrant coral reefs. Protecting these diverse ecosystems is crucial for the country’s biodiversity and the well-being of its people. Its national park system plays a vital role in this effort, safeguarding a treasure trove of flora and fauna. These parks offer a glimpse into Mexico’s rich natural heritage, providing opportunities for recreation, research, and conservation.Mexico’s national parks are more than just scenic spots; they are vital components of the country’s ecological integrity.
Their preservation ensures the continued existence of unique ecosystems, supports local communities, and provides opportunities for scientific discovery and environmental education.
Ecosystem Diversity
Mexico’s national parks encompass a remarkable variety of ecosystems. From the arid deserts of the north to the lush rainforests of the south, and the vibrant coastal areas, the country’s parks represent a microcosm of the nation’s natural beauty. These varied environments provide habitats for an extraordinary range of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region.
This biodiversity is a significant asset, providing valuable ecological services and contributing to the overall health of the planet.
Comparison of National Parks
| Park Name | Size (sq km) | Location | General Climate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yucatán Peninsula National Parks | Approximately 10,000 sq km | Eastern Mexico, bordering the Caribbean Sea | Subtropical, warm and humid, with a pronounced wet and dry season |
| Copper Canyon National Park | Approximately 700 sq km | Northern Mexico, within the Sierra Madre Occidental | Arid to semi-arid, with significant temperature variations between day and night |
| Nevado de Toluca National Park | Approximately 300 sq km | Central Mexico, in the state of Mexico | Varied, from temperate to alpine, with cooler temperatures at higher elevations |
This table provides a snapshot of the geographical dimensions and climates of some prominent Mexican national parks. The size and location directly influence the types of ecosystems found within them and the specific challenges involved in their conservation.
Top 5 Most Visited National Parks
These parks are highly popular destinations for visitors seeking adventure, relaxation, and a connection with nature. Their diverse attractions make them must-see destinations for both domestic and international tourists.
- Iztaccíhuatl-Popocatépetl National Park: This park is renowned for its iconic twin volcanoes, offering stunning views and opportunities for hiking and exploration. The unique geological features and the park’s high elevation create a captivating environment. The area provides a unique perspective on the geological forces that have shaped Mexico’s landscape.
- Copper Canyon National Park: Famous for its breathtaking canyon system, it’s a paradise for adventure enthusiasts. Hiking trails, scenic overlooks, and opportunities for exploring the unique flora and fauna of the region make it a favorite among tourists. The canyon’s depth and scale offer a remarkable display of nature’s grandeur.
- Yucatán Peninsula National Parks: These parks showcase the region’s diverse ecosystems, including ancient Mayan ruins, cenotes, and abundant wildlife. Visitors can explore the rich history and natural beauty of the region, including the unique cave systems and the unique biodiversity of the area. The Yucatán Peninsula is a vibrant destination that blends cultural and natural attractions.
- Nevado de Toluca National Park: This park features diverse ecosystems, from alpine meadows to pine forests, offering a variety of activities like hiking, wildlife observation, and enjoying the natural beauty. The park provides a fascinating example of the interplay between different ecological zones at various altitudes.
- Los Tuneles National Park: This park offers visitors the opportunity to explore caves and tunnels, which are rich in biodiversity. The park provides an experience of exploring underground environments and witnessing the unique ecosystems adapted to these subterranean conditions. The park is a fascinating example of a unique ecosystem.
These five parks represent a small sample of the incredible diversity found within Mexico’s national park system. Each park offers a unique experience that showcases the country’s natural splendor and cultural heritage.
Exploring Specific Parks
Mexico boasts a remarkable array of national parks, each with unique ecosystems and captivating stories. Delving deeper into these protected areas reveals a wealth of biodiversity, geological wonders, and cultural significance. From the dramatic cliffs of Copper Canyon to the vibrant coral reefs of the Yucatán Peninsula, these parks offer a glimpse into the country’s diverse natural heritage.These parks are vital for conservation efforts, safeguarding fragile ecosystems and preserving Mexico’s rich tapestry of life.
Their exploration provides invaluable insights into the country’s ecological balance and the intricate relationship between nature and culture.
Mexico boasts some incredible national parks, from the vibrant jungles to the stunning deserts. Planning a trip to explore these natural wonders? For a truly unforgettable weekend getaway, consider experiencing the charm of Vilnius, Lithuania, with its rich history and beautiful architecture. Check out this itinerary for the ultimate weekend in Vilnius, Lithuania. Once you’ve had your fill of European charm, you can head back to Mexico and immerse yourself in the awe-inspiring biodiversity of its national parks.
Copper Canyon National Park: A Geological Marvel
Copper Canyon, a breathtaking natural wonder, is characterized by its profound geological features. Carved by the Rio Yaqui over millennia, the canyon’s sheer cliffs and deep valleys are a testament to the power of erosion. The park’s diverse landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to lush riparian zones, create a complex and captivating environment. Its unique geological formations are a significant attraction for geologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
The canyon’s sheer scale and the varied rock formations are a result of the interplay between tectonic forces and the erosive power of the river.
Yucatán Peninsula National Parks: A Biodiversity Hotspot
The Yucatán Peninsula is renowned for its unique biodiversity. The region’s national parks, encompassing diverse ecosystems, harbor a wealth of plant and animal life. From the ancient Mayan ruins to the dense jungle forests, the peninsula offers a rich and vibrant ecological landscape. This region’s diverse habitats support a surprising array of species, including numerous endangered species.
Mexico boasts some incredible national parks, offering stunning landscapes and diverse wildlife. If you’re looking for a delicious and meat-free alternative while exploring, I highly recommend checking out the meat free munching herbivores guide amsterdam for some great options in Amsterdam. It’s fascinating to see how many delicious, plant-based options exist, and it’s great to know there are similar opportunities to discover when you’re visiting other countries like Mexico.
The variety of ecosystems in Mexican parks is really inspiring.
The rich biodiversity is directly linked to the unique geological history and climatic conditions of the peninsula.
Mexico’s national parks are absolutely stunning, offering incredible biodiversity and breathtaking landscapes. However, before you pack your bags for a similar island getaway, it’s crucial to be aware of some key factors when traveling to the Gili Islands. Things to know before traveling to gili islands will help you prepare for the unique culture and environment.
Ultimately, planning ahead for any destination, whether it’s the vibrant jungles of Mexico or the serene beauty of the Gili Islands, ensures a truly unforgettable trip. Exploring Mexico’s best national parks should be on everyone’s bucket list.
Sierra Madre Oriental National Parks: Ecological Significance
The Sierra Madre Oriental national parks play a crucial role in safeguarding Mexico’s biodiversity. The diverse ecosystems within these parks, from pine forests to cloud forests, support a remarkable variety of flora and fauna. These parks act as vital ecological corridors, connecting various ecosystems and facilitating species migration. The ecological significance of the Sierra Madre Oriental parks extends beyond the park boundaries, influencing the surrounding regions.
They serve as crucial reservoirs of biodiversity and help maintain the health of the entire region.
Wildlife Summary Table
| Park | Common Wildlife | Endangered Species | Ecological Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Canyon | Jaguars, deer, various bird species, bats | Mexican wolf, Sonoran pronghorn | Crucial habitat for migratory birds and large mammals; supports biodiversity across varied altitudes. |
| Yucatán Peninsula | Mammals like tapirs, jaguars, monkeys; reptiles; diverse bird species; marine life | Hawksbill sea turtle, Mexican black howler monkey | Critical for maintaining coastal ecosystems; supports a wide range of species, including migratory and endemic ones. |
| Sierra Madre Oriental | Bears, tapirs, monkeys, diverse bird species | Mexican wolf, ocelot | Vital for connecting diverse ecosystems; supports high levels of biodiversity, acting as a corridor for migration. |
Indigenous Communities and National Parks
Many national parks in Mexico have a deep historical and cultural connection to indigenous communities. These communities have a profound understanding of the natural world and have a long history of interacting with the environment. For example, the Mayan people of the Yucatán Peninsula have a deep-rooted connection to the natural resources and spiritual significance of the region’s forests and cenotes.
This connection underscores the importance of incorporating indigenous knowledge and perspectives into conservation efforts. Their traditional practices often provide invaluable insights into sustainable resource management.
Activities and Experiences
Mexican national parks offer a diverse range of experiences for visitors, from thrilling hikes to serene wildlife encounters. These protected areas provide a unique opportunity to connect with nature and immerse oneself in the country’s rich biodiversity. Exploring these parks responsibly and safely is crucial for both personal enjoyment and the preservation of these valuable ecosystems.
Recreational Activities
Mexican national parks cater to a wide array of interests. Hiking trails, often ranging in difficulty, allow visitors to explore diverse landscapes. From gentle strolls through meadows to challenging ascents to mountain peaks, the choices reflect the park’s topography. Camping is another popular activity, offering opportunities to sleep under the stars and fully experience the natural surroundings.
Wildlife viewing, with its chance to observe native species in their habitat, is another highlight. Specialized tours and guides often enhance these experiences.
Safety Measures and Precautions
Safety is paramount when exploring Mexican national parks. Staying informed about weather conditions, trail difficulty, and potential hazards is essential. Carrying appropriate gear, such as water, sunscreen, and sturdy footwear, is critical for comfort and safety. It is highly recommended to inform someone of your itinerary and expected return time. Be mindful of wildlife and maintain a safe distance.
Following park regulations and guidelines is vital for the safety of everyone.
Responsible Tourism
Responsible tourism plays a crucial role in preserving the natural beauty and biodiversity of Mexican national parks. Minimizing environmental impact, respecting wildlife, and adhering to park regulations are essential aspects of responsible tourism. Reducing waste, properly disposing of trash, and staying on marked trails are examples of environmentally conscious practices. Respecting the natural habitat and avoiding interactions that could harm or disturb wildlife is essential.
Resources for Planning Trips
Several resources can assist visitors in planning their trips to Mexican national parks. The official websites of the parks provide detailed information about regulations, maps, and necessary permits. Local travel agencies and tour operators can offer insights and assistance with planning. Online forums and communities dedicated to outdoor activities often feature valuable insights from experienced visitors.
Accommodation Options Near Specific Parks
| Park | Accommodation Type | Description | Pricing Range (USD per night) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yucatán Peninsula National Parks | Eco-lodges | Sustainable, nature-immersive accommodations, often featuring unique architectural styles. | $50-$250 |
| Sierra Madre Occidental National Parks | Rustic Cabins | Basic but comfortable cabins, often located in remote areas, offering a connection to nature. | $30-$150 |
| Pacific Coast National Parks | Boutique Hotels | Modern hotels offering comfortable amenities, often located near beaches or coastal areas. | $100-$500 |
| Lake Chapala National Parks | Airbnb rentals | Various options for rentals, from private rooms to entire houses, often providing a home-like atmosphere. | $40-$200 |
Note: Pricing ranges are estimates and may vary depending on the specific accommodation, season, and availability.
Conservation Efforts
Protecting Mexico’s stunning national parks requires a multifaceted approach involving government agencies, dedicated funding, and proactive measures against threats. These efforts are crucial not only for preserving the natural beauty of these areas but also for safeguarding the biodiversity and cultural heritage they encompass. The challenges are significant, ranging from pollution and illegal activities to the need for consistent financial support.
Success stories demonstrate that conservation is achievable through collaboration and sustained commitment.The Mexican government plays a pivotal role in the protection of its national parks. Various agencies are responsible for enforcing environmental regulations, managing resources, and promoting sustainable tourism within these protected areas. Effective implementation of these policies requires a consistent and adequate budget, which enables the agencies to maintain infrastructure, hire personnel, and conduct necessary research and monitoring.
Insufficient funding can cripple these efforts, leading to a decline in park conditions and hindering the protection of valuable ecosystems.
Government Agencies and Regulations
Mexican government agencies, such as the Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT), are responsible for enforcing environmental laws and regulations within national parks. These agencies oversee permits, monitor activities, and enforce penalties for violations. Their mandate includes protecting biodiversity, regulating tourism, and controlling access to sensitive areas. Furthermore, collaboration with local communities is essential for effective conservation, as it fosters a sense of shared responsibility and participation in the protection of these valuable natural resources.
Funding for Conservation Initiatives
Adequate funding is crucial for the successful implementation of conservation initiatives. Financial support allows for the implementation of necessary programs, including park maintenance, research, staff salaries, and the development of sustainable tourism strategies. Without sufficient funding, efforts to combat pollution, illegal logging, and other threats are significantly hampered. Examples of successful conservation programs demonstrate that substantial investments in infrastructure and human resources yield positive outcomes, improving the condition of the protected areas and creating opportunities for sustainable development.
Threats to National Parks
Several threats endanger the integrity of Mexico’s national parks. Pollution, whether from industrial activities or inadequate waste management, negatively impacts air and water quality, affecting plant and animal life. Illegal logging, a common issue in many areas, disrupts forest ecosystems, reduces biodiversity, and often involves the illegal trade of valuable timber. Invasive species, introduced through various means, can outcompete native plants and animals, disrupting natural balance and impacting biodiversity.
Overtourism, while bringing economic benefits, can lead to environmental damage if not managed sustainably.
Addressing Threats and Successful Conservation Programs
Several initiatives are implemented to combat these threats. Stricter enforcement of environmental regulations and increased monitoring of protected areas are vital components of these strategies. Furthermore, community involvement plays a key role in conservation efforts, educating local populations about the importance of environmental protection and encouraging sustainable practices. The establishment of sustainable tourism models that minimize environmental impact while generating economic benefits for local communities is also crucial.Examples of successful conservation programs in Mexico’s national parks include initiatives focused on reforestation, waste management, and the development of sustainable tourism models.
These programs have shown that collaborative efforts between government agencies, local communities, and private organizations can result in positive environmental outcomes, demonstrating the potential for long-term protection and sustainable use of these valuable natural resources.
Visual Representation of Mexico’s Parks: Mexico Best National Parks
Mexico’s national parks offer a breathtaking panorama of natural beauty, showcasing diverse landscapes, vibrant ecosystems, and unique geological formations. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Madre to the sun-drenched beaches of the Pacific coast, each park whispers tales of resilience and biodiversity. These protected areas provide crucial habitat for countless species and offer invaluable opportunities for exploration and appreciation of nature’s artistry.
A Glimpse into the Majesty of the Copper Canyon
The Copper Canyon, a breathtaking spectacle of nature’s artistry, unfolds before the visitor like a vast, sculpted canvas. Imagine cascading waterfalls plunging into emerald pools, surrounded by towering cliffs that seem to pierce the sky. The sheer scale of the canyon is awe-inspiring; the depths are immeasurable, the sheer walls dropping down in dramatic folds. The sun, filtering through the towering rock formations, paints the canyon walls in shifting hues of gold and crimson.
This is a place where the grandeur of nature is on full display.
Flora and Fauna of the Sierra Madre
The Sierra Madre mountain range boasts a rich tapestry of plant life, a testament to the diverse climates found within its embrace. From the towering pines and firs of the higher altitudes to the vibrant flowers and shrubs that carpet the lower slopes, the flora of the Sierra Madre reflects the gradient of the environment. A symphony of colors and textures surrounds the visitor.
Wildlife is abundant. Majestic mountain lions, graceful deer, and elusive jaguars roam the forests, their presence a silent reminder of the wilderness’s strength and beauty. The symphony of bird songs echoes through the trees, adding a vibrant melody to the scene. The varied ecosystems within the Sierra Madre, from pine forests to cloud forests, support a wide array of species, each playing its part in the delicate balance of nature.
Geological Marvels of the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, a land of ancient Mayan ruins and stunning natural beauty, presents a unique geological story. The landscape is dominated by karst topography, a telltale sign of the region’s unique geological history. Sinkholes, known as cenotes, are a characteristic feature of the area, revealing the porous nature of the limestone bedrock beneath. These crystal-clear cenotes, often filled with vibrant aquatic life, are both beautiful and mysterious.
The caves and caverns that lie beneath the surface offer further evidence of the fascinating interplay of water and rock over millennia. These caverns reveal a world hidden beneath the surface, where stalactites and stalagmites create breathtaking formations.
Ecosystem Diversity of the Pacific Coast Reserves
The Pacific Coast reserves boast a range of ecosystems, each with its own unique character. From the lush rainforests that cling to the slopes of the mountains to the vibrant coral reefs teeming with life, the coast is a vibrant mosaic of life. The intertidal zones, where land meets sea, offer a glimpse into the dynamic interplay of marine and terrestrial life.
This coastal region displays a variety of ecosystems that are vital for a multitude of species. The varied landscapes of the coastal regions, from beaches to mangroves to rocky shorelines, create an area of significant biological importance.
Diverse Landscapes and Terrain of the Baja California, Mexico best national parks
Baja California’s diverse terrain is a testament to the region’s unique geological history. From the rugged, desert landscapes of the interior to the dramatic cliffs and beaches of the coast, the region offers a stunning array of environments. The dramatic elevation changes create different climatic zones, fostering a wide array of plant and animal life. The peninsula’s unique topography, shaped by tectonic forces and the constant interplay of land and sea, creates a spectacle of varied and captivating beauty.
The juxtaposition of desert scrubland and coastal wetlands, of mountains and valleys, makes Baja California a truly captivating and diverse region.
Comparison of Parks
Mexico boasts a remarkable array of national parks, each unique in its ecosystems, attractions, and historical significance. Comparing these parks reveals not only their individual beauty but also the diverse approaches to conservation and sustainable tourism employed across the country. This comparison will focus on two prominent examples, highlighting their similarities and differences.A deep dive into these contrasting parks reveals valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing sustainable tourism in Mexico’s natural heritage.
By analyzing their management strategies, historical context, and the experiences they offer, a more comprehensive understanding of Mexico’s national park system emerges.
Comparing Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac and Izta-Popo National Park
These two parks, while geographically distant, represent distinct facets of Mexico’s natural and cultural heritage. Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac, nestled in the state of Morelos, showcases a blend of ecological and historical significance. Izta-Popo, spanning two states, presents a dramatic high-altitude landscape with volcanic features. Both parks offer unique experiences for visitors, while also facing their own challenges and opportunities for sustainable tourism.
Ecosystems and Attractions
Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac, with its historical ties to the ancient Nahua people, encompasses a diverse range of ecosystems. From cloud forests to temperate zones, the park offers diverse flora and fauna. Its attractions include the stunning archaeological sites, reflecting the region’s rich cultural past. Izta-Popo, on the other hand, is dominated by a high-altitude volcanic landscape. Visitors are drawn to the challenging hiking opportunities, panoramic views from the peaks, and the unique flora and fauna adapted to the extreme conditions.
Management Strategies
Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac’s management focuses on preserving its cultural heritage, balancing historical preservation with ecological conservation. The park employs strategies to promote sustainable tourism, including educational programs and visitor restrictions in sensitive areas. Izta-Popo’s management prioritizes the preservation of the volcanic ecosystem and the protection of its unique flora and fauna. This involves monitoring wildlife populations, controlling access to sensitive areas, and raising awareness among visitors.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Tourism
Both parks face challenges in balancing visitor numbers with environmental protection. Overcrowding in Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac can strain resources and impact delicate ecosystems. Izta-Popo’s remote location and challenging terrain present unique logistical challenges in terms of visitor access and waste management. Opportunities exist in developing eco-friendly tourism packages, implementing responsible waste management systems, and enhancing visitor education.
Historical Significance
Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac’s historical significance lies in its connection to the ancient Nahua civilization. The park’s archaeological sites offer invaluable insights into their cultural practices and beliefs. Izta-Popo, with its imposing volcanic peaks, holds cultural significance in indigenous traditions and mythology. The park’s high-altitude environment also provides a glimpse into the diverse ecological adaptations of the region.
Unique Experiences
Cuidad Cuauhnáhuac offers a unique cultural immersion, allowing visitors to connect with Mexico’s rich history through its archaeological sites and cultural heritage. Izta-Popo offers an unparalleled opportunity for adventurous travelers seeking challenging hikes and breathtaking views of the surrounding landscapes. Each park provides a distinctive experience, reflecting the diversity of Mexico’s natural and cultural heritage.
Final Wrap-Up
From the breathtaking Copper Canyon to the diverse ecosystems of the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico’s national parks showcase the country’s natural wonders. Understanding the importance of responsible tourism and conservation efforts ensures these incredible destinations remain vibrant for generations to come.