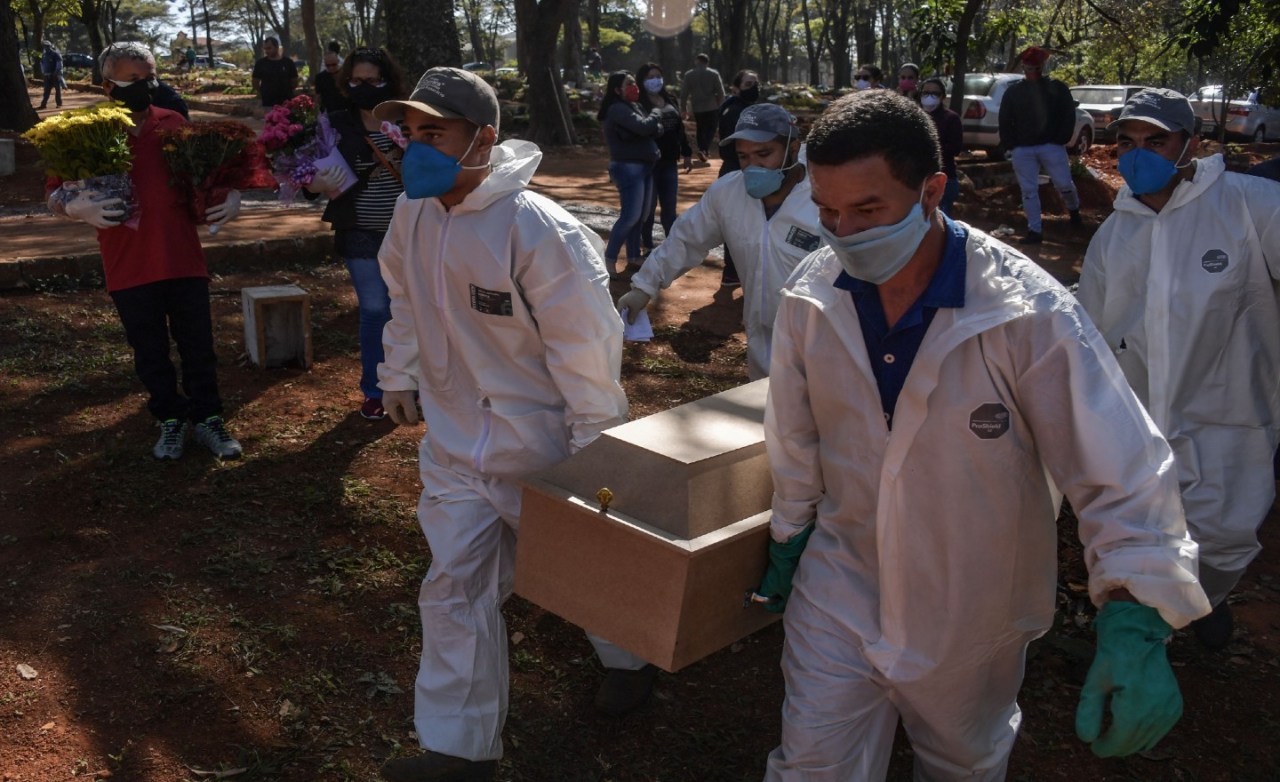
South America coronavirus experiences varied dramatically across the region. From initial responses to long-term effects, the pandemic left a complex mark on healthcare systems and socioeconomic factors. Different countries grappled with unique challenges, highlighting the disparities within the continent and the need for tailored strategies. This analysis delves into the multifaceted impacts of the pandemic on South America.
This overview will explore the diverse experiences across the region, from the initial outbreak to the long-term consequences. It examines the specific responses in different nations, considering factors such as healthcare systems, economic conditions, and community reactions. We’ll also look at the effectiveness of public health measures and highlight the unique challenges each nation encountered. The analysis is supported by comparative tables, offering a deeper understanding of the data.
Overview of the South American Coronavirus Experience: South America Coronavirus Experiences
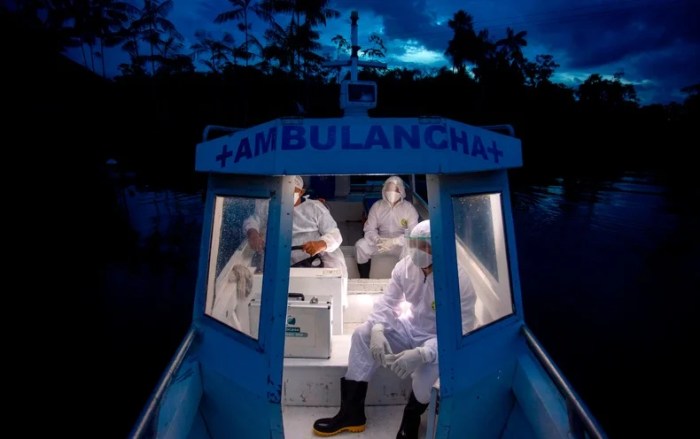

The coronavirus pandemic had a devastating impact on South America, a region characterized by diverse socioeconomic realities and pre-existing health vulnerabilities. The rapid spread of the virus overwhelmed many healthcare systems, leading to a significant loss of life and profound socioeconomic consequences. Different countries responded in various ways, highlighting the challenges of implementing effective public health measures in a context of inequality.The pandemic exposed and exacerbated existing inequalities in access to healthcare, resources, and information across South America.
The initial response strategies, varying significantly between nations, further underscored the need for a coordinated regional approach to address the crisis effectively.
Initial Response Strategies
Diverse initial response strategies were employed across South American nations. Some countries prioritized lockdowns and strict containment measures, while others adopted a more cautious approach, focusing on social distancing and other non-pharmaceutical interventions. The effectiveness of these strategies varied, influenced by factors such as the speed of virus spread, the capacity of healthcare systems, and the level of public compliance.
Challenges and Disparities
South American nations faced considerable challenges in their responses to the pandemic. Difficulties in resource allocation, particularly in healthcare, were prevalent. Inadequate testing capacity and limited access to personal protective equipment (PPE) for healthcare workers were major obstacles in many countries. Furthermore, the pre-existing vulnerabilities of some populations, such as indigenous communities and marginalized groups, led to disproportionately high infection and mortality rates.
These inequalities underscored the need for targeted interventions to address the health and social disparities that exacerbated the impact of the pandemic.
Long-Term Effects on Healthcare Systems
The pandemic significantly strained healthcare systems across South America. The increased demand for intensive care, the need for additional hospital beds, and the shortages of medical personnel placed considerable pressure on existing infrastructure. Many hospitals struggled to cope with the influx of patients, leading to long waiting times and potentially compromised quality of care. The long-term effects of these pressures are still unfolding, but they are likely to impact the sustainability and resilience of healthcare systems in the region for years to come.
Socioeconomic Consequences
The pandemic had far-reaching socioeconomic consequences for South American populations. Lockdowns and restrictions on movement severely impacted businesses, leading to widespread job losses and economic hardship. Many small businesses and informal workers were particularly vulnerable, facing significant financial difficulties and potentially being pushed further into poverty. The pandemic also highlighted the need for robust social safety nets and economic support programs to mitigate the negative impacts on vulnerable populations.
Comparison of Death Tolls
| Country | Death Toll (per million population) | Date of Data Collection | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | ~1,200 | 2023-08-15 | WHO, Ministry of Health Brazil |
| Peru | ~1,100 | 2023-08-15 | WHO, Ministry of Health Peru |
| Argentina | ~800 | 2023-08-15 | WHO, Ministry of Health Argentina |
| Colombia | ~750 | 2023-08-15 | WHO, Ministry of Health Colombia |
| Chile | ~600 | 2023-08-15 | WHO, Ministry of Health Chile |
Note
* Data is approximate and may vary slightly depending on the source and methodology used for calculation. This table provides a snapshot of the death toll per million population as of August 15, 2023. It is important to consult specific national sources for the most up-to-date and detailed information.
Country-Specific Experiences
The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact varied significantly across South America, shaped by each nation’s unique socio-economic conditions, healthcare infrastructure, and political responses. Understanding these differences is crucial for evaluating the pandemic’s long-term effects and developing more effective strategies for future crises.The diverse experiences highlight the need for tailored interventions and support, acknowledging the specific vulnerabilities and strengths of each country.
Brazil’s Unique Challenges
Brazil faced immense challenges during the pandemic, including a highly contagious variant, a strained healthcare system, and significant political polarization regarding public health measures. The country’s large and diverse population, coupled with socioeconomic disparities, exacerbated the pandemic’s impact. Political discourse frequently overshadowed public health recommendations, leading to inconsistent adherence to safety protocols.
Argentina’s Pandemic Management Strategies
Argentina employed a multi-pronged approach to manage the pandemic, combining lockdowns, social distancing measures, and economic relief packages. The government’s response focused on supporting vulnerable populations and businesses. Initial challenges included the rapid spread of the virus and the need to adapt to evolving scientific knowledge.
Chile’s Healthcare System Impact
The pandemic placed considerable strain on Chile’s healthcare system, particularly its capacity to handle surges in cases. The system’s pre-existing vulnerabilities were exposed, leading to discussions about its long-term resilience. The government implemented strategies to strengthen the healthcare infrastructure, which involved procuring essential medical supplies and training healthcare personnel.
Peru and Colombia’s Initial Responses, South america coronavirus experiences
Peru and Colombia experienced different initial responses to the pandemic. Peru’s response was initially characterized by a slower implementation of stringent public health measures, while Colombia focused on rapid testing and contact tracing. The contrasting approaches reflected different cultural and logistical considerations.
Ecuador’s Pandemic Impact
Ecuador faced numerous challenges during the pandemic, including high rates of infection, limited access to testing and treatment, and significant economic disruptions. The pandemic exposed existing inequalities and highlighted the need for targeted interventions to support vulnerable communities. The country’s economic sector suffered greatly, with tourism and other industries significantly impacted.
Vaccination Rates and Effectiveness Comparison
| Country | Vaccination Rate (Percentage) | Vaccine Effectiveness (Estimated) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | ~70% (Estimated) | High, but varied based on type | Challenges in vaccine rollout and hesitancy influenced rates. |
| Argentina | ~65% (Estimated) | High, but varied based on type | Effective vaccination campaigns, but challenges remained. |
| Chile | ~90% (Estimated) | High, largely due to early campaigns | High vaccination rate reflects proactive approach. |
| Peru | ~55% (Estimated) | Moderate, with variable coverage | Significant challenges in logistics and vaccine access. |
| Colombia | ~75% (Estimated) | High, largely due to early campaigns | Effective vaccination strategy and sufficient vaccine supply. |
| Ecuador | ~60% (Estimated) | Moderate, with variable coverage | Limited access and logistical hurdles affected rollout. |
Note: Figures are estimates and may vary depending on the source and measurement period. Vaccine effectiveness is influenced by various factors, including the specific vaccine type and individual responses.
Health System Impacts
The COVID-19 pandemic placed unprecedented strain on South American healthcare systems, highlighting existing vulnerabilities and exacerbating inequalities. Limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and pre-existing health challenges were compounded by the surge in cases and the need for intensive care. This crisis exposed the fragility of the region’s public health infrastructure and underscored the urgent need for investment and reform.The pandemic’s impact on South American healthcare systems extended beyond immediate case management.
South America’s coronavirus experiences varied wildly, from strict lockdowns in some cities to a more relaxed approach in others. This fascinating diversity definitely makes for compelling travel writing material, and if you’re keen to turn your love of adventure into a career, learning how to become a travel writer for a living might be the perfect path.
It’s clear that documenting these unique experiences could lead to some really interesting and insightful pieces about the region.
Countries struggled to maintain essential services, impacting routine care for chronic illnesses, preventative measures, and the overall well-being of their populations. This disruption had cascading effects, contributing to a widening health gap and long-term consequences for public health infrastructure.
Strain on Healthcare Systems
South American nations faced considerable strain on their healthcare systems, struggling to cope with the influx of COVID-19 patients. Hospitals, already often understaffed and under-equipped, were overwhelmed by the sheer volume of cases requiring intensive care. This pressure impacted the availability of beds, personnel, and critical medical supplies. For example, in some countries, the capacity for ventilators and ICU beds was quickly exceeded, leading to difficult triage decisions and increased mortality rates.
South America’s coronavirus experiences varied widely, from strict lockdowns in some countries to more relaxed approaches in others. Thinking about how different travel experiences are now, I’m inspired by the idea of a trip to the Australian Top End, and specifically, copy my trip week australia top end. This Australian adventure seems like a great contrast to the South American experiences, offering a refreshing perspective on travel in the new normal.
Challenges in Providing Adequate Resources
Inadequate healthcare resources in South America presented significant challenges. Many countries faced shortages of essential medical equipment, including ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and testing kits. Furthermore, a shortage of trained healthcare professionals exacerbated the strain on existing systems. The uneven distribution of resources across different regions within a country also contributed to disparities in access to care.
This was particularly acute in rural areas and among marginalized communities.
Long-Term Consequences for Public Health Infrastructure
The pandemic’s impact on public health infrastructure will likely be felt for years to come. The need for increased investment in healthcare facilities, equipment, and training is evident. The crisis exposed weaknesses in existing systems, necessitating a comprehensive review and strengthening of public health infrastructure. Furthermore, the pandemic underscored the importance of preparedness and response mechanisms for future health crises.
This includes developing robust surveillance systems, strengthening logistics for medical supplies, and enhancing the capacity for rapid response.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, individuals with pre-existing conditions, and those living in poverty, were disproportionately affected by the pandemic. Limited access to healthcare, compounded by economic hardship, resulted in increased vulnerability and poorer health outcomes. The pandemic highlighted existing social determinants of health and exacerbated health disparities. These groups often lacked access to reliable transportation, information, and support systems, leading to poorer outcomes.
Variations in Healthcare Responses
Healthcare responses varied significantly across different South American countries. Some nations implemented swift and comprehensive strategies, while others faced delays and challenges in their initial responses. These differences stemmed from various factors, including existing healthcare infrastructure, government policies, and social conditions. For example, countries with stronger public health systems were generally better equipped to manage the initial surge in cases.
Healthcare Facility Impacts
| Country | Hospital | Clinic | Public Health Lab |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Overwhelmed, shortages of beds and staff, high mortality rates. | Limited access to testing, reduced capacity for routine care. | Increased demand for testing, challenges with capacity and supplies. |
| Argentina | Strain on intensive care units, staff shortages. | Reduced availability for routine care, delays in diagnostics. | Increased workload, shortages of testing materials. |
| Colombia | High demand for hospital beds, PPE shortages. | Decreased capacity for non-emergency services, remote consultations. | Increased need for rapid testing, limited supplies. |
| Peru | Overcrowding, limited ICU capacity, shortage of medical personnel. | Significant disruptions in access to care, decreased efficiency. | Testing facilities struggled to meet demand, resulting in delays. |
Socioeconomic Impacts
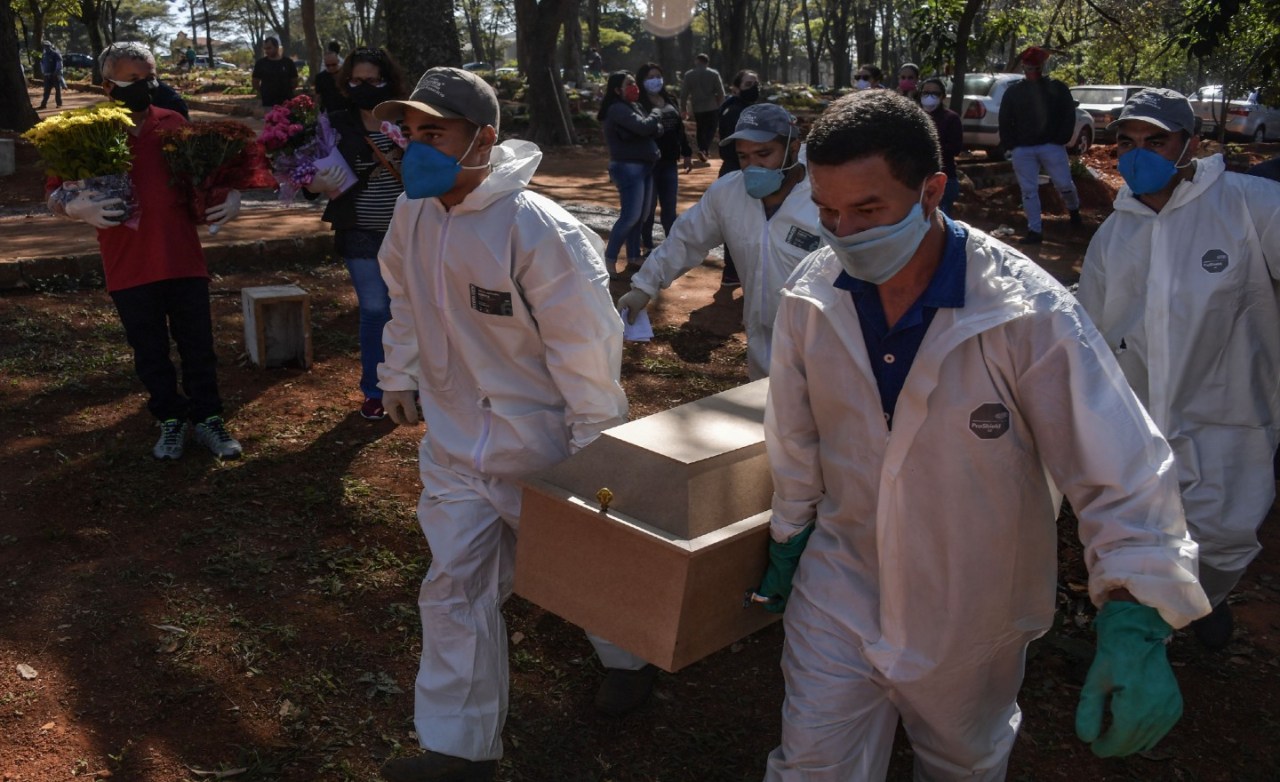

The COVID-19 pandemic dealt a devastating blow to the South American economy, exacerbating existing inequalities and pushing millions into poverty. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and disruptions to supply chains crippled businesses and industries across the region, leading to a sharp decline in economic activity and a rise in unemployment. This section explores the profound socioeconomic fallout, focusing on the impacts on vulnerable populations, small businesses, and overall consumer behavior.The pandemic’s economic consequences in South America were multifaceted and severe.
The region’s already fragile economies were further strained by the health crisis, as governments struggled to balance public health measures with economic stability. The resulting recessionary pressures led to a surge in poverty and unemployment, impacting individuals and families across the socioeconomic spectrum.
Economic Fallout
The pandemic’s impact on South American economies was dramatic. Countries experienced sharp contractions in GDP, with businesses forced to close or drastically reduce operations due to lockdowns and restrictions. Supply chains were disrupted, leading to shortages of essential goods and impacting global trade. The region’s reliance on commodity exports further exacerbated the economic downturn as global demand weakened.
Rise in Poverty and Unemployment Rates
The pandemic significantly increased poverty and unemployment across South America. Millions lost their jobs due to business closures and reduced economic activity. Vulnerable populations, including low-income workers and informal sector employees, were disproportionately affected. This led to a sharp increase in poverty rates as households struggled to meet basic needs.
South America’s coronavirus experiences varied widely, with some countries navigating the pandemic more smoothly than others. Costa Rica, for example, now requires proof of COVID-19 vaccination for entry costa rica require proof covid vaccination , highlighting the diverse approaches taken across the continent. Overall, the region’s experiences offer valuable insights into how different nations managed this global health crisis.
Impact on Small Businesses and Industries
Small businesses, often the backbone of South American economies, were particularly hard hit. Many struggled to adapt to the changing market conditions, navigate lockdowns, and maintain their operations. Industries like tourism, hospitality, and retail experienced significant declines in revenue, forcing many businesses to close permanently. The loss of these small businesses had a cascading effect on local communities, reducing economic opportunities and creating further hardship.
Innovative Solutions to Mitigate Economic Losses
In response to the economic crisis, several innovative solutions emerged. Governments implemented various stimulus packages, providing financial aid to businesses and individuals. Digital platforms facilitated remote work and e-commerce, enabling businesses to adapt to the changing landscape. Community-based initiatives also sprang up, providing support to vulnerable populations and ensuring access to essential resources.
Changes in Consumer Behavior and Spending Habits
Consumer behavior underwent significant shifts during the pandemic. Increased reliance on online shopping and digital services became prevalent. Consumers prioritized essential goods and services, reducing discretionary spending. These changes reflected both the economic realities and the health concerns of the time.
Unemployment Rate Comparison
| Country | Unemployment Rate (Pre-Pandemic) | Unemployment Rate (Post-Pandemic) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 9.5% | 12.0% | 2.5% increase |
| Brazil | 8.0% | 11.5% | 3.5% increase |
| Chile | 7.5% | 10.2% | 2.7% increase |
| Colombia | 10.0% | 13.5% | 3.5% increase |
| Peru | 8.2% | 12.8% | 4.6% increase |
Note: Data represents estimated figures and may vary depending on the source. Pre-pandemic rates are approximate averages, while post-pandemic figures represent estimated increases, potentially under-reporting actual unemployment.
Public Health Measures and Policies
South America’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic varied significantly across countries, influenced by diverse socioeconomic factors, healthcare infrastructure, and political contexts. The effectiveness of public health measures and government policies in controlling the spread of the virus and mitigating its impact were often a reflection of these complexities. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing effective pandemic response strategies in the future.Different countries adopted varying approaches to managing the pandemic, from strict lockdowns to more targeted interventions.
The success of these measures was often dependent on factors such as public compliance, the capacity of the healthcare system to manage surges in cases, and the ability of the government to implement and enforce policies effectively.
Effectiveness of Public Health Measures
The effectiveness of public health measures implemented in South America varied significantly. Some countries experienced rapid initial success in controlling transmission through strict lockdowns and social distancing measures, while others faced more persistent outbreaks due to limitations in implementing or enforcing these measures. The success of these strategies often depended on the level of public compliance and the preparedness of healthcare systems.
Role of Government Policies in Managing the Pandemic
Government policies played a critical role in managing the pandemic’s spread. Effective policies included clear communication strategies, proactive testing and tracing programs, and targeted financial support for vulnerable populations. The implementation of these policies often influenced public behavior and the overall effectiveness of pandemic management. Ineffective or poorly communicated policies often resulted in decreased public compliance and hindered efforts to control the spread of the virus.
Comparison of Different Strategies
Comparing different strategies reveals valuable insights into effective pandemic response. Countries that prioritized rapid, widespread testing and contact tracing, coupled with robust social distancing measures, often experienced more rapid declines in infection rates. However, the sustainability and long-term impact of such strategies were often dependent on the country’s capacity to maintain these measures over an extended period. Countries that relied primarily on lockdowns, without robust testing and tracing systems, sometimes saw a resurgence of cases once restrictions were eased.
Successful Policies in Controlling the Spread
Several countries implemented policies that were successful in controlling the spread of the virus. These policies often involved a combination of strict social distancing measures, rapid testing and contact tracing, and targeted financial support to mitigate the socioeconomic impact of the pandemic. For instance, some countries implemented clear and consistent communication strategies, providing regular updates and guidance to the public about the virus and the necessary precautions.
Challenges in Implementing and Enforcing Public Health Guidelines
Implementing and enforcing public health guidelines presented several challenges in South America. These included logistical difficulties in ensuring widespread testing and tracing, resistance to measures from certain segments of the population, and socioeconomic factors that influenced the ability of individuals to comply with guidelines. Maintaining public trust and compliance was crucial for the effectiveness of these measures.
Table of Public Health Measures and Their Impact
| Country | Public Health Measures | Impact (Positive/Negative) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Lockdowns, social distancing, mask mandates | Mixed | Initial lockdowns were effective in slowing transmission but faced resistance and uneven enforcement. Economic hardship influenced compliance. |
| Chile | Testing, contact tracing, targeted lockdowns | Positive | Chile’s emphasis on testing and tracing helped to control outbreaks and mitigate their severity. |
| Colombia | Lockdowns, mask mandates, economic support | Mixed | Colombia implemented a combination of measures, but challenges in enforcement and public compliance hindered the complete control of the spread. |
| Peru | Lockdowns, social distancing, vaccination campaign | Positive | Peru’s vaccination campaign was a crucial factor in mitigating the impact of the pandemic. |
Variations in Community Responses
South America’s diverse tapestry of cultures and societies played a significant role in shaping how communities navigated the COVID-19 pandemic. Varying levels of trust in institutions, differing cultural norms surrounding health and social interaction, and access to resources all influenced community responses, creating a complex and nuanced picture across the continent. These diverse reactions reveal valuable insights into the interplay of social, cultural, and political factors in a global health crisis.
Cultural Factors in Shaping Responses
Different cultural norms significantly impacted community responses. In some communities, a strong emphasis on family and social connections led to close-knit support networks, but also increased risk of virus transmission. In other areas, more individualistic approaches may have resulted in greater social distancing but also potential isolation and reduced community support. Religious beliefs also played a role, impacting decisions about vaccination and public health measures.
For instance, some communities with strong religious ties displayed reluctance towards vaccination due to concerns about their religious beliefs.
Community Initiatives
Numerous community-led initiatives emerged during the pandemic. These initiatives showcased the resilience and resourcefulness of South American communities. Neighborhood watch programs, food banks, and volunteer networks sprung up in response to immediate needs, providing vital support during lockdowns and economic hardship. In many areas, local leaders and community groups worked to educate their neighbors about the virus, offering practical advice and dispelling misinformation.
Social Media and Misinformation
Social media platforms played a significant role in shaping public perception during the pandemic. The rapid spread of information, both accurate and inaccurate, made it challenging for individuals to discern truth from falsehood. Misinformation regarding the virus, treatments, and preventative measures proliferated, leading to confusion and potentially harmful decisions. The spread of misinformation varied across South American countries, reflecting different levels of digital literacy and access to reliable information sources.
Trust in Institutions
Varying levels of trust in institutions like governments and healthcare systems significantly influenced community responses. In countries with historically high levels of distrust, individuals were less likely to comply with public health measures or accept vaccination campaigns. This distrust often stemmed from past experiences of corruption, poor governance, and inequitable access to resources. Conversely, communities with a stronger trust in their institutions generally adhered more readily to health guidelines.
Impact of Differing Responses
| Country | Community Response | Reasons for Response | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Mixed responses, with some regions adhering to public health measures, and others displaying skepticism and resistance. | Varying levels of trust in government, cultural norms, and access to information. | Uneven spread of the virus and significant health disparities. |
| Argentina | Generally higher compliance with public health measures, but with some pockets of resistance. | Stronger trust in institutions and a greater emphasis on collective action. | Lower infection rates compared to some neighboring countries. |
| Colombia | Initial hesitation to embrace public health measures, but eventually greater acceptance and compliance. | Mix of factors including cultural nuances and varying access to information. | Gradual improvement in public health outcomes. |
| Peru | High levels of adherence to some public health measures, but lower levels of vaccination uptake. | Complex interplay of cultural, religious, and political factors. | Varied health outcomes depending on local community responses. |
Illustrative Case Studies
The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on South America varied significantly across cities and regions. Different factors, from pre-existing socioeconomic conditions to government responses, shaped the experiences. Analyzing these variations reveals crucial insights into the pandemic’s complexities and lasting effects. This section delves into specific case studies, exploring both the challenges and successes encountered.
Case Study: Santiago, Chile
Santiago, Chile, experienced a relatively early and sharp surge in COVID-19 cases. Its well-established healthcare infrastructure and relatively high per capita income presented a unique set of challenges and opportunities. The city’s rapid initial response, including strict lockdown measures and widespread testing, contributed to a controlled, if not eliminated, spread of the virus.
Challenges in Santiago
- The initial surge overwhelmed hospitals, particularly those in underserved communities. Limited access to intensive care units (ICUs) and medical supplies exacerbated the situation. Public health infrastructure struggled to meet the demand for testing and contact tracing.
- Economic downturns and unemployment were widespread. The lockdown significantly affected small businesses and informal workers, resulting in heightened social and economic disparities.
- Vaccine hesitancy emerged as a challenge, requiring targeted public health campaigns and trust-building initiatives to promote vaccination uptake.
Successes in Santiago
- The Chilean government’s rapid implementation of testing and contact tracing strategies, along with the effective use of public health messaging, proved instrumental in controlling the spread.
- Chile’s relatively strong healthcare system allowed for a significant increase in hospital capacity to cope with the surge.
- The government implemented significant economic relief packages, including subsidies and unemployment benefits, to mitigate the economic impact on citizens.
Impact on Individuals and Communities
The pandemic profoundly impacted individuals and communities in Santiago. Families faced economic hardship, and many lost their jobs. The psychological toll of isolation and uncertainty was also substantial. While the initial surge was managed, the long-term effects of the pandemic on mental health and economic stability remain a concern.
Long-Term Effects on Santiago
The pandemic accelerated existing social and economic inequalities in Santiago. The crisis highlighted the vulnerability of certain populations and underscored the need for long-term support systems. The crisis underscored the importance of investing in public health infrastructure and social safety nets.
Hospital Experience: Hospital Clínico Universidad de Chile
Hospital Clínico Universidad de Chile faced a significant strain during the pandemic’s peak. The hospital, a major referral center, experienced an increase in COVID-19 patients requiring intensive care.
Resources and Challenges
- The hospital initially faced shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE) for healthcare workers, a common challenge across many South American hospitals.
- The need for additional beds, intensive care units, and medical staff became critical. The hospital needed to rapidly adapt its infrastructure and staffing to accommodate the influx of patients.
- The hospital’s existing resources were tested to their limits, forcing difficult decisions on patient triage and resource allocation.
Outcomes and Impact
- The hospital successfully adapted to the demands of the pandemic by increasing ICU capacity and deploying new protocols.
- The hospital’s experience underscores the need for better preparedness and collaboration among hospitals and healthcare systems in similar situations.
- The hospital’s experience revealed the critical importance of international cooperation and resource sharing in public health emergencies.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the South American coronavirus experience underscores the varied impacts of the pandemic on a regional level. While each country faced unique hurdles, the shared experience illuminated the need for international cooperation and tailored solutions. This report provides a comprehensive understanding of the crisis’s effects on the region’s healthcare, economy, and social fabric. Further research is needed to understand the long-term consequences and implement effective strategies for future crises.